Electric Vehicle charger is also known as electric vehicle supply equipment (EVSE). The EVSE is the basic unit of EV charging infrastructure.
The EVSE accesses power from the local electricity supply and utilizes a control system and wired connection to safely charge EVs
Electric vehicles (EV) can be charged in a variety of ways, depending on location and requirement. Accordingly, charging infrastructure for EVs is of different types and designed for different applications.
Specifications and standards for EV chargers, also known as electric vehicle supply equipment (EVSE),vary from one country to another, based on available EV models in the market and the characteristics of the electricity grid.
CHARACTERISTICS OF EVSE – EV SUPPLY EQUIPMENT
Electric vehicle supply equipment (EVSE) is the basic unit of EV charging infrastructure.
The EVSE accesses power from the local electricity supply and utilizes a control system and wired connection to safely charge EVs.
An EVSE control system enables various functions such as user authentication, authorization for charging, information recording and exchange for network management, and data privacy
and security.
It is recommended to use EVSEs with at least basic control and management functions, for
all charging purposes.
Conductive charging, or plug-in (wired) charging, is the mainstream charging technology in use.
Requirements of EVSE for conductive charging depend on factors such as vehicle type, battery capacity, charging methods, and power ratings.
Best Handheld Home Electric Vehicle Chargers
- Zevpoint Portable EV Charger/ Ropeset for Cars
- Portable EV Charger Fast 7.4kW (32A) with LCD Display Current Adjustment and 5 Meter Cable
- Zevpoint Swift Pro Electric Vehicle Charger | 7.2 kW, Type 2 Connector, Single Phase, 20 feet Cable | Touch Screen, Power Control, Smart
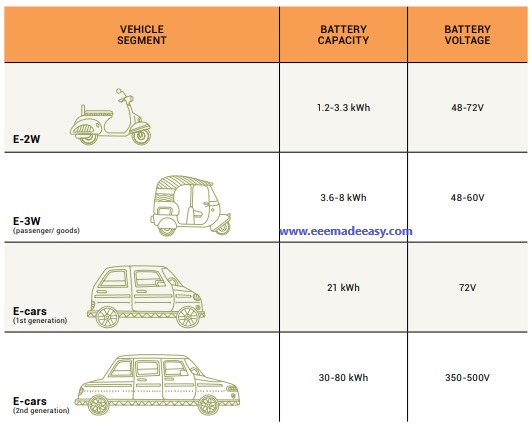
BATTERY SPECIFICATIONS OF DIFFERENT EV SEGMENTS
In India, transport electrification over the next decade is expected to be driven by light electric vehicles (LEVs), comprising two-wheelers (scooters, motorcycles) and three-wheelers (passenger and cargo).
Apart from these, cars and light commercial vehicles (LCVs) are the other key vehicle segments being electrified.
Electric buses will also be present in significant numbers.
| VEHICLE SEGMENT | BATTERY CAPACITY | BATTERY VOLTAGE |
|---|---|---|
| E-2W | 1.2-3.3 kWh | 48-72V |
| E-3W (passenger/ goods) | 3.6-8 kWh | 48-60V |
| E-cars (1st generation) | 21 kWh | 72V |
| E-cars (2nd generation) | 30-80 kWh | 350-500V |
EV charging requirements depend on the specifications of EV batteries, as power must be
supplied to the battery at the right voltage and current levels to permit charging.
Typical capacity and voltage of EV batteries vary among the different EV segments,
as shown in Table.
E-2Ws and e-3Ws are powered by low-voltage batteries.
The first generation of e-cars is also powered by lowvoltage batteries. However, these are likely to be phased out in the future, even if they continue in specific use cases such as taxis.
The second generation of e-cars, as seen in the upcoming e-car models, is powered by
high-voltage batteries.
Electric LCVs will comprise of both low-voltage and high-voltage vehicles, depending
on their load-carrying capacity.
Battery Specifications for EV Segments
Read more on Electric Vehicles
- Electric Vehicle
- Electric Vehicle Terminologies
- Electric Vehicle Charging Standards
- Charging Methods & Power Ratings for Electric Vehicles
- Electric Vehicle charger|EVSE- Electric Vehicle Supply Equipment
Download & Install EEE Made Easy App
Latest Posts in EEE Made Easy
- RRB JE CBT 2 Exam Date 2025 Postponed|RRB JE CBT 2 Exam Date
- [PDF]RRB JE Result 03/2024 Cut off, Selected no of candidates for all regions
- [PDF]Final Answer Key Junior Instructor Mechanic Agricultural Machinery|643/2023 Solved Question paper
- Acoustics MCQs|Industries Extension officer|IEO 2025
- LASER MCQs| Industries Extension officer|IEO 2025
- Practical Types of Capacitors
- [PDF] Syllabus JUNIOR INSTRUCTOR MECHANIC AGRICULTURAL MACHINERY|643/2023 Syllabus Kerala PSC