In this post we can discuss the causes of low power factor , Effect of low power factor, and what is the need for power factor improvement.
What is Power Factor?
Cause and effect of low power factor and methods for pf improvement
The heating and lighting loads supplied from a 3-phase supply have power factors, ranging from 0.95 to unity.
But motor loads have usually low lagging power factors, ranging from 0.5 to 0.9.
Single-phase motors may have as low a power factor as 0.4 and electric wedding units have even lower power factors of 0.2 or 0.3.
The power factor is given by
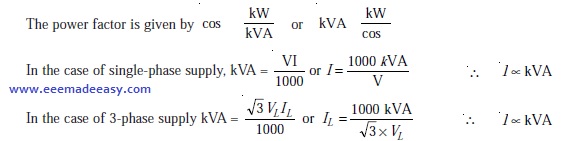
In each case, the kVA is directly proportional to current. The chief disadvantage of a low p.f. is that the current required for a given power, is very high.
Download & Install EEE Made Easy App
Causes of low power factor
a) The presence of harmonic current in the system reduces power factor.
b) Improper wiring leads to three-phase imbalance causing low power factor.
c) When the system is loaded lightly, the voltage increases, increasing the magnetization current demand of the machine.
Effect of low power factor (p.f)
- A Low P.F. draws a higher internal current and the excessive heat generated will damage and/or shorten equipment life
- Increased reactive loads can reduce output voltage and damage equipment sensitive to reduced voltage
disadvantages of Low Power Factor
disadvantages of Low Power Factor in our electrical system are
- Large kVA rating and size of Electrical equipments
- Large conductor size and so higher cost of transmission line
- High Transmission loss hence poor efficiency
- Poor Voltage regulation
- Penalties imposed by power utility companies
(i) Large kVA for given amount of power
All electric machinery, like alternators, transformers, switchgears and cables are limited in their current-carrying capacity by the permissible temperature rise, which is proportional to I2.
Hence, they may all be fully loaded with respect to their rated kVA, without delivering their full power. Obviously, it is possible for an existing plant of a given kVA rating to increase its earning capacity
(which is proportional to the power supplied in kW) if the overall power factor is improved i.e. raised.
(ii) Poor voltage regulation
When a load, having allow lagging power factor, is switched on, there is a large voltage drop in the supply voltage because of the increased voltage drop in the supply lines and transformers.
This drop in voltage adversely affects the starting torques of motors and necessitates expensive voltage stabilizing equipment for keeping the consumer’s voltage fluctuations within the statutory limits. Moreover, due to this excessive drop, heaters take longer time to provide the desired heat energy, fluorescent lights flicker and incandescent lamps are not as bright as they should be. Hence, all supply undertakings try to encourage consumers to have a high power factor
Power factor Correction Equipments
Power factor correction (PFC) aims to ;
- improve power factor and therefore
- improve power quality.
- Reduction of the load on the electrical distribution system
- increases energy efficiency and
- reduces electricity costs.
The following equipment is generally used for improving or correcting the power factor :
(i) Synchronous Motors (or capacitors)
These machines draw leading kVAR when they are over-excited and, especially, when they are running idle.
They are employed for correcting the power factor in bulk and have the special advantage that the amount of correction can be varied by changing their excitation.
(ii) Static Capacitors
They are installed to improve the power factor of a group of a.c. motors and are practically loss-free (i.e. they draw a current leading in phase by 90°).
Since their capacitances are not variable, they tend to over-compensate on light loads, unless arrangements for automatic switching off the capacitor bank are made.
(iii) Phase Advancers
They are fitted with individual machines.
However, it may be noted that the economical degree of correction to be applied in each case, depends upon the tariff arrangement between the consumers and the supply authorities
Download & Install Job Search India App for daily Job Updates
- RRB JE CBT 2 Exam Date 2025 Postponed|RRB JE CBT 2 Exam Date
- [PDF]RRB JE Result 03/2024 Cut off, Selected no of candidates for all regions
- [PDF]Final Answer Key Junior Instructor Mechanic Agricultural Machinery|643/2023 Solved Question paper
- Acoustics MCQs|Industries Extension officer|IEO 2025
- LASER MCQs| Industries Extension officer|IEO 2025
- Practical Types of Capacitors
- [PDF] Syllabus JUNIOR INSTRUCTOR MECHANIC AGRICULTURAL MACHINERY|643/2023 Syllabus Kerala PSC
- [PDF] Syllabus JUNIOR INSTRUCTOR WOOD WORK TECHNICIAN|674/2023 Syllabus Kerala PSC
- [PDF] Syllabus JUNIOR INSTRUCTOR MECHANIC CONSUMER ELECTRONIC APPLIANCES|670/2023 Syllabus Kerala PSC
- [PDF] Junior Instructor Hospital Housekeeping| 646/2023 syllabus Kerala PSC
- [PDF] Syllabus Workshop Instructor Tool and Die|242/2023 syllabus Kerala PSC
- [PDF]Junior Instructor Technician Mechatronics Syllabus|654/2023 syllabus Kerala PSC