
In this post, we will discuss about Electrical measuring instruments. Types of measuring instruments: Absolute Instruments & Secondary Instruments, Moving Iron & Moving Coil Instruments,(a) Indicating instruments, (b) Integrating instruments, (c) Recording instruments.
Measuring Instruments
The basic electrical quantities which often need to be measured are ;
voltage, current, energy. power, electrical power factor, frequency, resistance, inductance capacitance, speed, temperature etc.
The instruments used for all electrical measurements are called measuring instruments.
General Principles of Measurement READ HERE
They include ammeters, voltmeters, watt- meters, energy meters etc.
Electrical Instruments
The instruments which are used to measure electrical quantities are called electrical instruments. Such as ammeter, voltmeter, wattmeter, energy meter, megger etc.
Characteristics of Instruments read HERE
The electrical instruments may be classified as,
(1) Absolute instruments, (2) Secondary instruments.
Absolute instruments
The instruments which give the value of the quantity to be measured in terms of the constants of the instrument are called absolute instruments.
Such instruments do not require any previous calibration.
A common example of this type of instrument is a tangent galvanometer.
Tangent galvanometer

The tangent galvanometer is an early measuring instrument for small electric currents.
It consists of a coil of insulated copper wire wound on a circular non-magnetic frame. Its working is based on the principle of the Tangent law of magnetism.
When a bar magnet is suspended in two Magnetic fields B and Bh, it comes to rest making an angle θ with the direction of Bh.
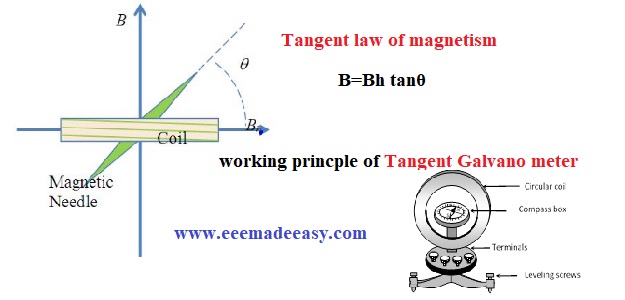
B=Bh tanθ. This is known as the tangent law of magnetism
When a current is passed through the circular coil, a magnetic field (B) is produced at the center of the coil in a direction perpendicular to the plane of the coil.
The tangent galvanometer is arranged in such a way that the horizontal component of earth’s magnetic field (Bh) is in the direction of the plane of the coil.
The magnetic needle is then under the action of two mutually perpendicular fields
Secondary instruments
The instruments which determine the electrical quantity to be measured directly in terms of deflection are called secondary instruments.
These instruments are generally used in practical life. They are further classified as;
(a) Indicating instruments, (b) Integrating instruments, (c) Recording instruments.
(a) Indicating instruments
The instruments which indicate the magnitude of electrical quantity being measured instantaneously are called indicating instruments.
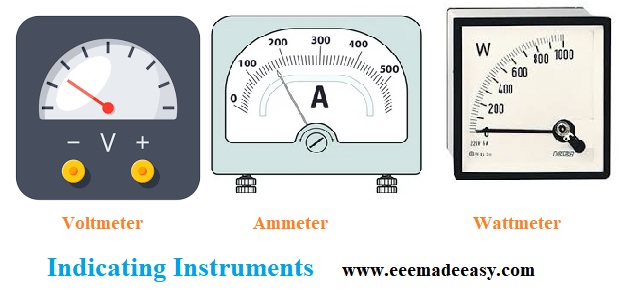
In such instruments, a pointer moves over the calibrated scale to indicate the magnitude of the electrical quantity being measured.
Examples of Indicating Instruments:Ordinary ammeters, volt meters, and watt meters fall into this category.
(b) Integrating instruments
The instruments which add up the electrical quantity, i.e., electrical energy and measure the total energy (in kWh) in a given period are called integrating instruments.

In such instruments, there are sets of dials or gears which register the total quantity of electricity or the total amount of electrical energy supplied to a circuit in a given period.
Example : Watt-hour Meter, Energy Meter
(c) Recording instruments
The instruments which give a continuous record of the variations of the electrical quantity being measured are called recording instruments.
Indicating Type Instruments
Indicating instuments are of the following types
(i) Moving iron instruments
(11) Moving coil instruments
(1i) Dynamometer type instruments
(iv) Hot wire instruments
(v) Electrostatic type instruments
(vi) Induction type instruments
Moving Iron Instruments
Moving Iron instruments are of two types-
1.Attraction type
2.Repulsion type
Attraction Type Moving Instruments
Attraction Type MI instruments are based on the principle that when an unmagnetized soft iron piece is placed in the magnetic field of a coil then the piece is attracted towards the coil.
The deflection is proportional to the square of current through the coil. Thus, the scale of such instruments in non-uniform being crowded in the beginning
Repulsion type Moving Instruments
These instruments are based on the principle of repulsion between the two iron pieces similarly magnetized.
Since deflection is proportional to the square of the current through the coil, therefore the scale of such instruments in non-uniform is crowded in the beginning.
Merits of Moving Iron Instruments
The moving iron instruments have the following advantages
1. These are cheap, robust, and simple in construction.
2. The instruments can be used for both A.C. as well as D.C. circuits.
3. These instruments have high operating torque.
4. These instruments are reasonably accurate.
disadvantages of moving iron instruments
Demerits-The following are the disadvantages of moving iron instruments
1.Such instruments have non-uniform scale.
2. These instruments are not very sensitive.
3. Errors are introduced due to change in frequency in case of A.C. measurements.
4. Higher power consumption.
Moving Coil Instruments
Moving coil instruments are of two types
- Permanent magnet type (used for D.C. only)
- 2. Dynamometer type (used for both A.C. and D.C, only)
Moving coil instruments works on the principle that “When a current-carrying conductor is placed in a magnetic field, it is acted upon by a force which tends to move it to one side and out of the field.”
Advantages of Moving coil instruments
1.Uniform scale
- Very effective eddy current damping
- No hysteresis loss
- Power consumption low
- As the working field is very strong. therefore such
instruments are not affected by stray fields - Such instruments require a small operating current
- Very accurate and reliable
Disadvantages of Moving coil instruments
Some errors are caused due to the aging of control springs.
More Posts on Measuring Instruments
- [PDF]Electrical Measurements Measuring Instruments Study Notes PDF|EMMI Notes EEE Made Easy
- MCQ on Electrical Instruments
- Types of Errors in Instruments| Instrument Errors
- MCQ’s on Electrical Measuring Instruments|Instruments Objective Questions
- Electrical measuring instruments|Types of Measuring Instruments
- Static characteristics of instruments
- Types of measuring instruments- www.eeemadeeasy.com
- Moving Iron Instruments
- Instruments- Basics
- PMMC Instruments
- Types of instruments
- Essentials of Indicating instruments
- MCQ’s on Galvanometer|Galavnometer Questions & Answers
- MCQs on potentiometer|potentiometer Questions and answers
- TOD Meter or Time of Day Meter
- Light meters or illumination meter|Lux meter
- VU and decibel meters
- Multimeter- Principle and operation
- Digital readout meters-principle and operation
- Watt-hour meters- principle and operation
- Wattmeter -principle and working
- FET and vacuum-tube voltmeters
- Ohmmeter- basic principle and working
- Ammeters|Current Measurement
- Voltmeter- Principle and operation
- The household energy meter is
- Q Meter
- Thermistor| What is a Thermistor
- RTD vs Thermistor|Comparison between RTD and Thermistor
Latest Posts in EEE Made Easy
- Environment MCQ for RRB JE CBT 2|Objective Questions Environment for Competitive Exams
- RRB JE CBT 2 Computer Awareness Book Arihant|Objective Computer Awareness Book 2025
- RRB JE CBT 2 Exam Date 2025 Postponed|RRB JE CBT 2 Exam Date
- [PDF]RRB JE Result 03/2024 Cut off, Selected no of candidates for all regions
- [PDF]Final Answer Key Junior Instructor Mechanic Agricultural Machinery|643/2023 Solved Question paper
- Acoustics MCQs|Industries Extension officer|IEO 2025
- LASER MCQs| Industries Extension officer|IEO 2025
Latest Posts in EEE Made Easy
- Environment MCQ for RRB JE CBT 2|Objective Questions Environment for Competitive Exams
- RRB JE CBT 2 Computer Awareness Book Arihant|Objective Computer Awareness Book 2025
- RRB JE CBT 2 Exam Date 2025 Postponed|RRB JE CBT 2 Exam Date
- [PDF]RRB JE Result 03/2024 Cut off, Selected no of candidates for all regions
- [PDF]Final Answer Key Junior Instructor Mechanic Agricultural Machinery|643/2023 Solved Question paper
- Acoustics MCQs|Industries Extension officer|IEO 2025
- LASER MCQs| Industries Extension officer|IEO 2025



