BASIC ELECTRICAL, ELECTRICITY
What is matter ?
A body which has a definite weight and which occupies some space is called matter.
What are the first 3 states of matter ?
Matter is found three states —solid, liquid and gas.
Download & Install EEE Made Easy App
What is a molecule ?
The smallest particle of a matter which contains all physical and chemical properties of that matter is called a molecule.
What is an atom ?
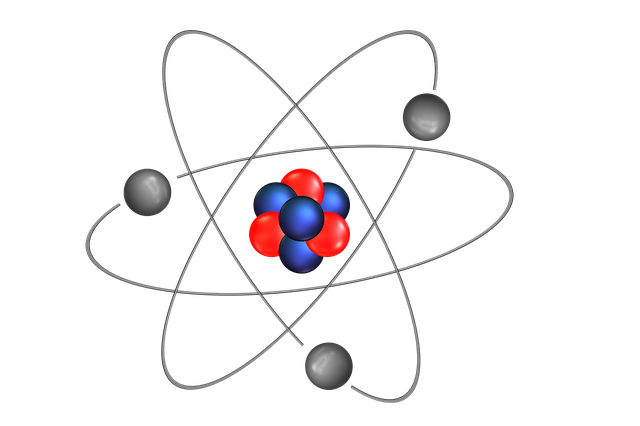
An atom is the smallest particle of matter which can take part in chemical reactions and can be separated by a chemical reaction but has no free existence.
What do you know about atomic structure ?
The central part of an atom is called the nucleus. It contains protons (positively charged particles) and neutrons (neutral particles). A number of electrons (negatively charged particles) revolve around the nucleus in different orbits.
Read : Electron Mass – Mass of electron, Charge, Speed, & value of electron
Which one is the simplest atom?
Hydrogen atom is the simplest atom. It consists of one proton and one electron only. The electron revolves around the proton.
What is an element ?
A matter composed of only one kind of atoms is called element.
How many types of elements are known ?
The no. of elements found on the earth is 94 and 24 elements have been developed artificially in laboratories.
What is a compound ?
A matter composed of two or more than two types of atoms is called a compound.
Which one is smallest out of electron, proton and neutron ?
Electron is the smallest particle. It is 1845 times lighter than a proton.
Do an electron and a proton have equal charge ?
Yes, an electron has a negative charge of 1.602 x 10^-19 coulombs while a proton has a positive charge of the same magnitude.
What is atomic number ?
The number of electrons or protons present in atom is referred as atomic number.
What is atomic weight ?
Atomic weight of an atom is equal to the number of protons plus the number of neutrons present in that atom.
How will you define an electron ?
An electron is the smallest particle of an atom. Electrons of all the substances are quite identical. It has a unit negative charge of 1.602 x 10^-19 coulombs.
What is current ?
Current is the flow of electrons.
What is the direction of current-flow?
The current is said to flow from a positively charged body to the negatively charged body, but the electrons actually move from negative to positive.
What is the unit of current ?
The unit of current is ampere. If the rate of flow of electrons is 6.28x 10^24 per second, the amount of current is said to be one ampere.
Read : 5 Basic Electrical Quantities|charge, Current, Voltage,Energy,Power|Electrical Elements
What is international ampere ?
The amount of current that can deposit 0.00118 grams silver per second at the cathode when passed through the solution of silver nitrate is called an international ampere.
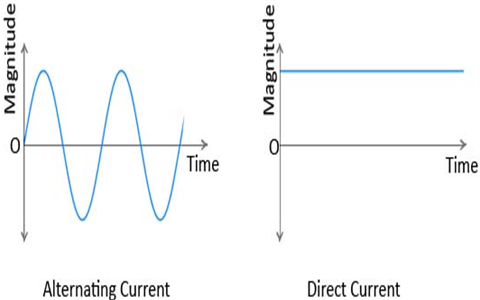
How many types of current ?
There two main types of curent-DC and AC.
What is DC ?
The current whose magnitude and direction remains constant s called DC or direct current.
What is AC ?
The current whose magnitude and direction remains alternating at definite rate is called AC or alternating current.
What are the main effects of electric current ?
There are three main effects of electric current. Heating, chemical and magnetic effects
Read: 3 Effects of Electric Current|Magnetic Effect, Heating Effect & Chemical Effects
What is the heating effect of current ?
A current-carrying conductor gets heated up because of electrical energy dissipation by the resistance of that conductor.
What is the chemical effect of current ?
The flow of current through certain solutions produces a chemical change in the composition of the solution, the phenomenon is referred as electrolysis.
What is the magnetic effect of current ?
A current carrying conductor produces a magnetic field around it.
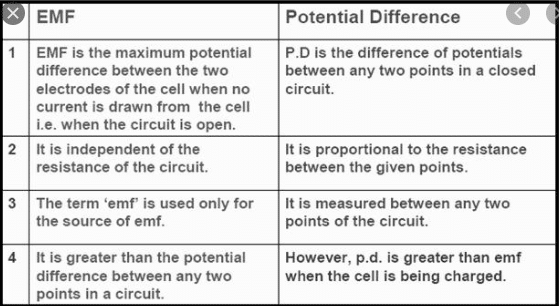
What is e.m.f.?
The electrical force which sets the electrons in motion is called emf or electro-motive force.
What is p.d.?
The difference of potential developed across a conductor due to flow of current through the conductor is called.d. or potential difference.
Read :5 Basic Electrical Quantities|charge, Current, Voltage,Energy,Power|Electrical Elements
What is potential ?
The electrical level of a conductor or the work done in moving a unit charge from infinity to that point is termed as potential. What is the unit of e.m.f. and p.d. volt.
What is one volt ?
It is as a pressure across a resistance of one ohm which causes one ampere of current to flow through that resistor.
What is resistance ?
The natural property of a substance that opposes the flow of current through it is called resistance.
What is the unit of resistance ?
ohm.
What is one ohm ?
If one ampere of current flows through a circuit at an applied e.m.f. of one volt, the resistance of the circuit is said to be one ohm.
Read : What is Ohm’s Law? Ohm’s Law Statement Formula Examples
What is the difference between e.m.f. and p.d. ?
If The amount of current flow of a circuit is zero, the magnitude of p.d. will also be zero but the e.m.f. will not be zero.
What is the speed of electric current ?
The speed of electric current is 3 x 10^8 m/s. (this is approximtaely near to speed of light. The speed of electricity depends on the conductor type also. The maximum possible is 99% of speed of light wave)
What is the static electricity ?
The electrical charge produced in a substance by friction is known as static electricity.
What is a conductor ?
A conductor is a substance that readily allows a current to flow through it.
What is an insulator ?
An insulator is a substance that does not readily allow a current to flow through it.
What is a semi-conductor ?
A semi-conductor is a substance which is neither a conductor or an insulator, e.g. germanium, silicon etc.
What are the properties of a good conductor ?
A good conductor should have a low resistance, low temperature co efficient, low cost and should be mechanically rigid, ductile and easily available.
What are the principal conductors?
Principal conductors are silver, copper, aluminium, lead, tin nichrome, eureka, tungsten, carbon, acidic solution etc.
Which is the best and economical conductor ?
Copper.
What are the properties of a good insulator ?
A good insulator should have high resistance, high dielectric strength, ability to bear high temperature and should be mechanically rigid, permanent moisture and water proof.
What are the principal insulators?
Principal insulators are Dry air, asbestos, bakelite, glass, mica, wax, slate, porcelain, rubber, plastic,xx mish, marble, P.V.C., cotton silk etc.
Which is the best insulator ?
Vulcanised rubber.
What is meant by dielectric strength ?
The voltage bearing capability of a dielectric (insulator) is called its dielectric strength. It is expressed in kilo volts per mm.
What is meant by breakdown voltage ?
The dielectric strength of an insulator is also generally referred as its breakdown voltage. difference is given below.
The difference is important, since the breakdown voltage will be larger for thicker materials and smaller for thinner materials, but the dielectric strength will (theo- retically) remain unchanged. Dielectric strength is thus more like a material property, and breakdown voltage is more like a system property
What is bitumen ?
Bitumen is a chemical compound which softens on heating and is used for filling the junction boxes. It acts as an insulator.
What is a cable ?
A cable is an insulation covered conductor.

What are the principal types of cables according to the insulation used?
They are V.I.R., P.V.C., flexible, enamelled etc.
What is meant by grade of cables ?
(i)Low voltage grade up to 250 volts.
(ii) Medium voltage grade upto 650 volts.
(iii) High voltage grade up to 11000 volts
What is meant by P.V.C. ?
P.V.C.means poly-vinyle-chloride. It is a carbonic compound which appears and acts as artificial rubber.
What is meant by PILCSTA?

PILCSTA means-paper insulated lead covered single tape a armoured cable.
What is nichrome ?
Nichrome is an alloy of 80% nickel and 20% chromium. It is used for making heating elements.
What is eureka ?
Eureka is an alloy of 40% nickel and 60% copper. It is used for making rheostats and wire-wound resistors.
What is soldering ?
Soldering is a process of giving a permanent nature to joint of wires by covering the joint with a metal-alloy of a low melting point.

How many types of solders you know?
Two types-hard solder and soft solder. A soldering set CHECK HERE
What is hard solder ?
It consists of copper, zinc and tin (spelter) or copper, zinc and silver (silver solder).
What is soft solder ?
Soft solder has a low melting point and consists of lead and tin in the ratio of 10% and 90% to 90% and 10%.
What is flux ?
Flux is a paste/powder meant for clearing the surface of the joint to be soldered.
How soldering is done ?
Soldering is done by electric soldering iron, blow lamp or by cup and ladle.
.What type of solder is used in soldering of the aluminium joints ?
ALCA-P or ALCA-Z solder and EYER-7 flux are used in soldering of the aluminium joints.
What precautions should be observed in soldering ?
The soldering iron bit and the joint should be well-cleaned.
What are the constituents of a flux?
They are-zinc-chloride, ammonium chloride, resin, borax, olive oil, til-oil etc.
Electrical wiring materials and Tools Questions and answers read HERE
Electrical Engineering MCQ’s HERE
Electrical Engineering Interview Questions HERE
Electrical Engineering previous Question papers Download HERE
Study Notes Download HERE
Electrical Interview Questions
- Electrical Engineering Interview Questions|Basic Electrical Engineering Questions & Answers
- Electrical Engineering Important Interview Questions and Answers
- 30 Electrical Engineering Interview Questions & answers- Set 1
- Basic Electrical Engineering Questions and short Answers
- Sub Engineer KSEB Interview Questions
- [Set 2]Electrical Engineering Interview Questions and Answers|Electrical Engineer Interview Questions and Answers
- [Set 3] Electrical Engineering Interview Questions and Answers| Electrical Interview Questions
- [Set 4]Electrical Engineering Interview Questions|Electrical Questions and Answers
- Electrical Power System Problems and Solutions
- AE KSEB Interview Questions|Basic Electrical Engineering Interview Questions
Latest posts
Latest Posts in EEE Made Easy
- RRB JE CBT 2 Exam Date 2025 Postponed|RRB JE CBT 2 Exam Date
- [PDF]RRB JE Result 03/2024 Cut off, Selected no of candidates for all regions
- [PDF]Final Answer Key Junior Instructor Mechanic Agricultural Machinery|643/2023 Solved Question paper
- Acoustics MCQs|Industries Extension officer|IEO 2025
- LASER MCQs| Industries Extension officer|IEO 2025
- Practical Types of Capacitors
- [PDF] Syllabus JUNIOR INSTRUCTOR MECHANIC AGRICULTURAL MACHINERY|643/2023 Syllabus Kerala PSC