Basic Electrical Quantities: The Basic electrical quantities are charge, current, voltage, power, and energy. Their units are Coloumb, Ampere, Volt, watts, and Jules respectively.
Basic Electrical Quantities
Charge
The unit of charge is the coulomb (C) where one coulomb is one ampere second.
(1 coulomb = 6.24 x 1018 electrons).
Read : Mass of Electron, proton, neutron|Charge of electron and Proton
coulomb definition
The coulomb is defined as the quantity of electricity that flows past a given point in an electric circuit when a current of one ampere is maintained for one second.
Thus, charge, in coulombs Q = It
where I is the current in amperes, and t is the time in seconds.
Download & Install EEE Made Easy App
If a current of 5 A flows for 2 minutes, find the quantity of electricity transferred?
Example 1
Solution:
Quantity of electricity Q = It coulombs
I = 5 A, t = 2 x 60 = 120 s
Hence, Q = 5 x120 = 600 C
Electric current
Electric current is the rate of flow of electric charges. Electrons are negatively charged particles and their flow in conductors results in electric current.
By definition, current, is the rate of flow of charge.
i = dq/dt
If Q is the amount of charge flowing through a conductor in T seconds, then current I is given by the expression,
I = Q/T
The unit of charge is Coulomb.
1 Coulomb = 6.24×1018 electrons.
The unit of current is Ampere(A). 1 Ampere= 1 Coulomb/sec.
What current must fl ow if 0.24 coulombs is to be transferred in 15 ms?
Example
Since the quantity of electricity, Q = It , then
I =Q /t
= 0.24 / (15 x10-3)
= 240/15 = 16 A
Read: 3 Effects of Electric Current|Magnetic Effect, Heating Effect & Chemical Effects
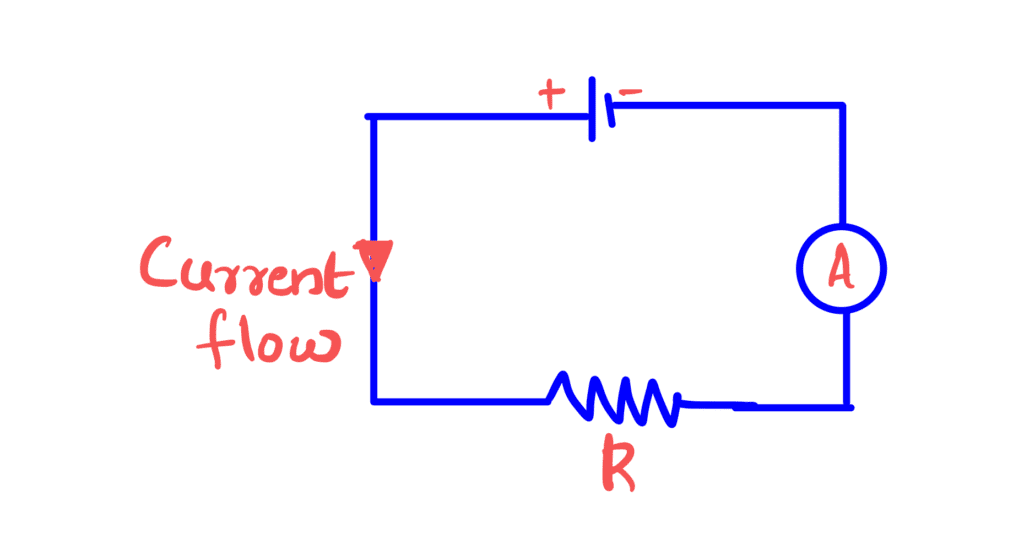
An ammeter is an instrument used to measure current and must be connected in series
with the circuit.
Since all the current in the circuit passes through the ammeter it must have a very low resistance.
If a current of 10 A fl ows for 4 minutes, find the quantity of electricity transferred?
Example
Solution
Quantity of electricity, Q = It coulombs
I = 10 A; t = 4 x 60 = 240 s
Hence, Q = 10 x 240 = 2400 C
Voltage
Electrical Potential and e.m.f. :The unit of electric potential is the volt (V) where one volt is one joule per coulomb.
Volt definition
One volt is defined as the difference in potential between two points in a conductor which,
when carrying a current of one ampere, dissipates a power of one watt, i.e.,
volts = watts / amperes
= (joules/second) /amperes
= joules / ampere seconds
= joules/coulombs
potential difference
A change in electric potential between two points in an electric circuit is called a
potential difference .
The electromotive force (e.m.f .) provided by a source of energy such
as a battery or a generator is measured in volts.
Potential Difference: For a continuous current to flow between two points in a circuit a potential difference or voltage, V, is required between them; a complete conducting path is necessary to and from the source of electrical energy.
The unit of voltage is the volt, V.
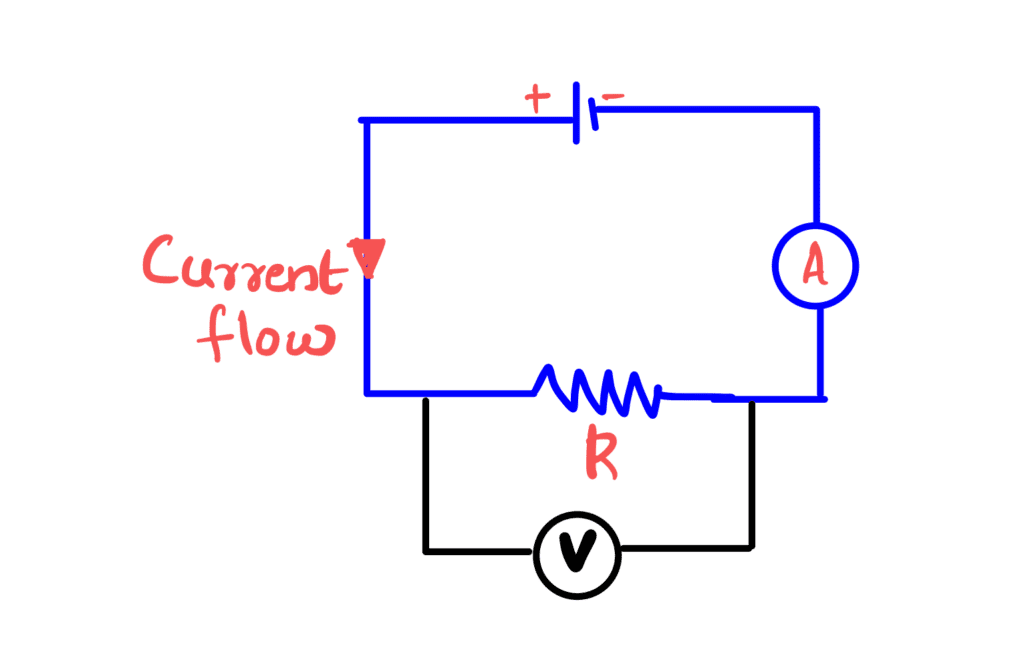
A voltmeter is an instrument used to measure voltage and must be connected in parallel
with the part of the circuit whose voltage is required.
To avoid a significant current fl owing through it, a voltmeter must have a very high resistance.
- FET and vacuum-tube voltmeters
- Voltmeter- Principle and operation
- Electrical measuring instruments|Types of Measuring Instruments
Electrical Power
Power P in an electrical circuit is given by the product of potential difference V and
current I. The unit of power is the watt , W .
Hence,
P = V x I watts ——(1)
From Ohm’s law, V = IR.
Substituting for V in equation (1) gives:
P = ( IR) x I
i.e., P = I2R watts
Also, from Ohm’s law, I = V/R
Substituting for I in the equation above gives:
P = V x (V/R)
i.e., P = V2R watts
There are three possible formulas that may be used for calculating power.
unit of power
The unit of power is the watt (W) where one watt is one joule per second.
Definition of power
Power is defined as the rate of doing work or transferring energy. Thus, power in watts, P =W/t
where W is the work done or energy transferred in joules and t is the time in seconds. Thus,
energy, in joules, W = Pt
A portable machine requires a force of 200 N to move it. How much work is done if the machine is moved 20 m and what average power is utilized if the movement takes 25 s?
Example 2
Solution:
Work done = force x distance
= 200 N x 20 m
= 4000 Nm or 4 kJ
Power = work done /time taken J/s
= 4000/25
= 160 J s 160W
Electrical Energy
Although the unit of energy is the joule, when dealing with large amounts of energy, the
unit used is the kilowatt hour ( kWh ) where,
1 kWh = 1000 watt hour
= 1000 x 3600 watt seconds or joules
= 3,600,000 J
Electrical energy = power X time
If the power is measured in watts and the time in seconds then the unit of energy is
watt-seconds or joules.
If the power is measured in kilowatts and the time in hours then the unit of energy is kilowatt-hours, often called the unit of electricity.
The electricity meter in the home records the number of kilowatt-hours used and is thus an energy meter.
A source e.m.f. of 5 V supplies a current of 3 A for 10 minutes. How much energy is provided in this time?
Example 3
Solution:
Energy = power x time , and power = voltage x current.
Hence,
Energy = VIt = 5 x 3 x (10 x 60)
= 9000 Ws or J
= 9 kJ
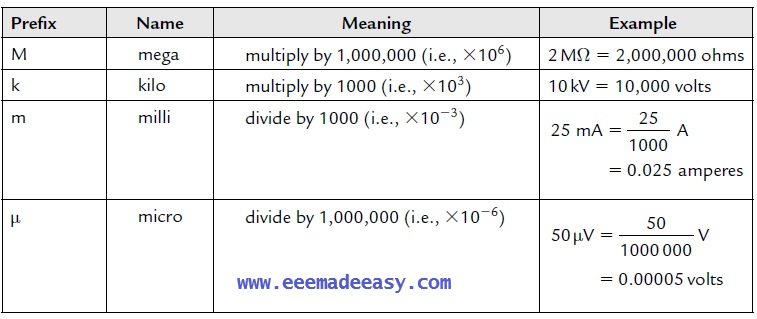
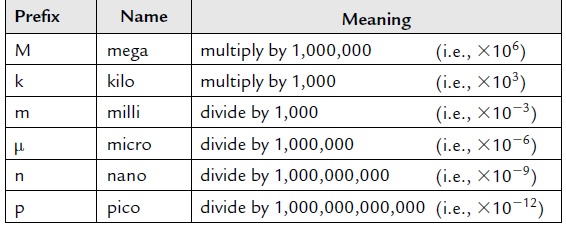
Common multiples and submultiples of units
Currents, voltages and resistances can often be very large or very small. Thus multiples
and submultiples of units are often used.
Latest Posts in EEE Made Easy
- Environment MCQ for RRB JE CBT 2|Objective Questions Environment for Competitive Exams
- RRB JE CBT 2 Computer Awareness Book Arihant|Objective Computer Awareness Book 2025
- RRB JE CBT 2 Exam Date 2025 Postponed|RRB JE CBT 2 Exam Date
- [PDF]RRB JE Result 03/2024 Cut off, Selected no of candidates for all regions
- [PDF]Final Answer Key Junior Instructor Mechanic Agricultural Machinery|643/2023 Solved Question paper
- Acoustics MCQs|Industries Extension officer|IEO 2025
- LASER MCQs| Industries Extension officer|IEO 2025