Electric Vehicle: An electric vehicle (EV) is a type of vehicle that uses one or more electric motors for propulsion, relying on electricity stored in batteries or another energy storage device.
Unlike traditional internal combustion engine vehicles that rely on gasoline or diesel, electric vehicles are powered by electricity, making them more environmentally friendly and energy-efficient.
Read Also: Electric Vehicle Terminologies
History of Electric Vehicles
The first Electric Vehicle was a small toy car that employed a primitive electric motor, built in
1828 by a Hungarian named Anyos Jedlik.
After that, some better working models of electric car, driven mainly by primary cells, was built in Scotland, Vermont (USA) and Netherlands by individuals.
Gaston Plante invented rechargeable lead–acid battery in 1859, making EVs viable for commercial purposes.
The first electric car production was started in London by inventor Thomas Parker in In Germany, first electric car was made by Andreas Flocken in 1888.
In the United States, William Morrison built the first car in 1891 that was powered by lead–
acid storage cells, having steering and a top speed of 20 miles/h .
EVs powered by lead–acid cells became popular in the late 1890s and early 1900s. Some of the popular names associated with EVs during this period are Karl Benz of Germany, Walter Bersey of Britain, Dr Ferdinand Porsche of Austria, Walter Baker of Ohio, and many more.
The decline in the popularity of EVs started by the 1920s when the discovery of large petroleum reserves all over the world led to the availability of cheap gasoline.
This led to the acceptance of Internal Combustion Engine (ICE) for vehicles. In the year 1912, the electric starter was invented by Charles Kettering to eliminate the difficult hand crank needed for cars with ICE.
Moreover, the mass production of ICE cars was started by Henry Ford in 1913, making them much cheaper than EVs which was another major blow to EVs. By the end of 1935, almost all EVs had disappeared from roads
Conventional vehicles and hybrid EVs
The ICE is considered conventional while EVs are modern vehicles as per the new needs of society.
The transition from conventional to Electric Vehicle is happening through a middle path chosen by a number of vehicle manufacturers like Hyundai, Honda, etc.
The philosophy for hybrid vehicles is to take benefit of both modes, reducing the weaknesses
existing in electrical vehicle technology.
The main drawback is the capacity of battery and its charging time and the related infrastructure.
Electric Vehicles are much expensive than their gasoline counterparts, and that is the main barrier for its adoption as pure Electric Vehicles at present.
The economics of these vehicles have forced the car manufacturer to adopt the hybrid
approach.
The day cost of gasoline reaches sufficiently high and the cost of battery and its charging cost reduce sufficiently low that the pure Electric Vehicles shall dominate the vehicle market.
At present, the hybrid EV is the preferred choice.
The four types of hybrid vehicles are possible: series hybrid, parallel hybrid, series–parallel, and complex hybrid.
you can read more on Typpes of Electric Vehicles in the next blog post.
Join EEE Made Easy Telegram channel
EV and major components
A pure Electric Vehicle essentially has a motor, a battery, and power electronic circuitry for efficient control.
An electric motor is used for propulsion that receives power from an onboard source of electricity which is a rechargeable battery or fuel cell.
The increase of efficiency in some EVs is done by additionally employing ultracapacitors
or flywheels.
It may or may not have the gear mechanism in it for power transmission. Even differential axles may also be absent in some designs.
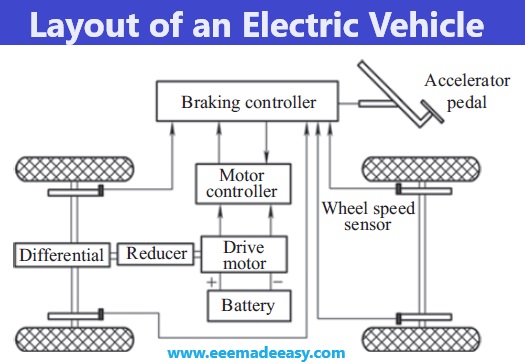
The layout of a typical EV is shown in Figure with its components.
Important components of the EV and their basic functions are discussed below.
Drive motor
The drive motor employed for an EV may be any motor among induction motor,permanent magnet brushless (PMBL) motor, switched reluctance motor (SRM), synchronous reluctance motor (SyRM), and other axial flux and magnet less motors.
The motor to be employed must have high efficiency and power density; therefore, brushless motors employing rare earth material-based permanent magnets like NdFeB are used.
Battery
The popular types of the batteries in the market are Lead–acid battery, Ni–Cd battery, Li–ion battery, metal–air batteries, etc.
The desired features of a battery are low cost, high specific energy, pollution free without carbon footprints, low specific weight, easy constituent chemical availability in abundance, fast charging, and long life.
The researchers are trying a number of alternatives and the features determining acceptance of a battery are compared with the corresponding characteristics of ICE fuel for it to be acceptable.
It seems at present the Li–ion batteries are the most preferred source for electric cars. It is desired that the battery should be able to power an Electric Vehicle for about 620 km continuously on one charge; however, at present, this is a distant reality.
Battery charging circuit
Charging of vehicle battery should be possible at home during the night; however, charging stations are needed during long-distance drives.
Alternatively, the power source for charging the battery may be PV supply or wind power.
Some wireless battery charging techniques are also proposed by the researchers through which batteries can be charged on roads at traffic lights.
Power electronic converters
Mainly efficient DC to DC or DC to AC or AC to DC converter topologies are needed. Converters based on vector control, direct torque control, etc. may be needed .
Regenerative braking must be employed.
Supercapacitors
The dynamic power supplies and sudden transient disturbance recovery should be possible by using suitable value supercapacitors having capacity values in the range of kilo Farads. These can be charged at much higher rates than a battery.
This has led to their suitability in power circuit configurations for EVs.
Flywheels
Flywheels may store kinetic energy in the form of their moment of inertia and return power back for charging a battery or driving wheel through suitable circuitry.
Energy management system
The energy management system (EMS) monitors control of required functions in an EV thereby acting as its brain.
It is a computer-based system that dynamically optimizes the charge of batteries to maximize the operating range and improve performance.
Regenerative braking system
If a battery has to have a better powering distance range, it must be efficiently used and, therefore, the regenerative braking is a necessary component of EVs.
Read more on Electric Vehicles
- Electric Vehicle
- Electric Vehicle Terminologies
- Electric Vehicle Charging Standards
- Charging Methods & Power Ratings for Electric Vehicles
- Electric Vehicle charger|EVSE- Electric Vehicle Supply Equipment
Join EEE Made Easy Whatsapp Channel
Best Handheld Home Electric Vehicle Chargers
- Zevpoint Portable EV Charger/ Ropeset for Cars
- Portable EV Charger Fast 7.4kW (32A) with LCD Display Current Adjustment and 5 Meter Cable
- Zevpoint Swift Pro Electric Vehicle Charger | 7.2 kW, Type 2 Connector, Single Phase, 20 feet Cable | Touch Screen, Power Control, Smart
FAQ on Electric Vehicles
what components of an electric vehicle are considered high voltage?
High Voltage Battery,High Voltage Cables,Service Plug or Switch etc are high voltage components of Electric vehicles
what is hybrid electric vehicle?
A hybrid electric vehicle (HEV) is a type of hybrid vehicle that combines a conventional internal combustion engine (ICE) system with an electric propulsion system
Which are the electric vehicle companies in india?
Olectra Greentech Ltd,Tata Motors Ltd,Mahindra Electric
Materials for Electric vehicle batteries
Materials for Electric vehicle batteries are Lithium, cobalt, graphite, nickel, and manganese
what are electric vehicle batteries made of?
electric vehicle batteries are mainly Li-ion Batteries
electric vehicle stocks in india
Olectra Greentech Ltd,Tata Motors Ltd,Exide Industries Ltd,Mahindra and Mahindra Ltd,Power Grid Corporation of India Ltd,Hero MotoCorp Ltd,Motherson Sumi Systems Ltd,Amara Raja Batteries Ltd
Download & Install EEE Made Easy App
Latest Posts in EEE Made Easy
- Environment MCQ for RRB JE CBT 2|Objective Questions Environment for Competitive Exams
- RRB JE CBT 2 Computer Awareness Book Arihant|Objective Computer Awareness Book 2025
- RRB JE CBT 2 Exam Date 2025 Postponed|RRB JE CBT 2 Exam Date
- [PDF]RRB JE Result 03/2024 Cut off, Selected no of candidates for all regions
- [PDF]Final Answer Key Junior Instructor Mechanic Agricultural Machinery|643/2023 Solved Question paper
- Acoustics MCQs|Industries Extension officer|IEO 2025
- LASER MCQs| Industries Extension officer|IEO 2025




