Magnetic data storage: Magnetic fields can be used to store data in different forms. Common media for data storage include the magnetic tape, the magnetic disk, and magnetic bubble memory.
Magnetic tape
Recording tape is the stuff you find in cassette players.
It is also sometimes seen on reel-to-reel devices.
These days, magnetic tape is used for home entertainment, especially hi-fi music and home video.
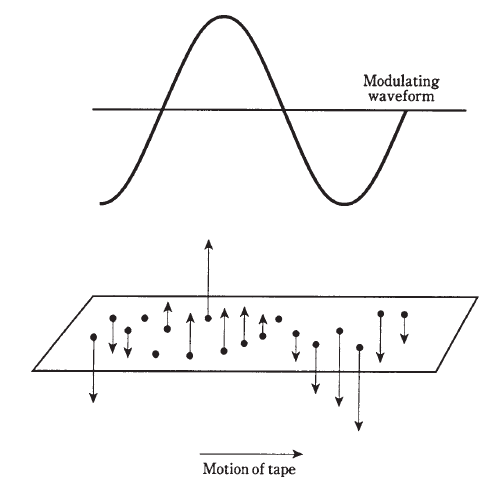
The tape itself consists of millions of particles of iron oxide, attached to a plastic or
mylar strip.
A fluctuating magnetic field, produced by the recording head, polarizes these particles. As the field changes in strength next to the recording head, the tape passes by at a constant, controlled speed.
This produces regions in which the iron-oxide particles are polarized in either direction.
When the tape is run at the same speed through the recorder in the playback mode,
the magnetic fields around the individual particles cause a fluctuating field that is detected
by the pickup head.
This field has the same pattern of variations as the original field from the recording head.
Magnetic tape is available in various widths and thicknesses, for different applications.
The thicker tapes result in cassettes that don’t play as long, but the tape is more
resistant to stretching.
The speed of the tape determines the fidelity of the recording.
Higher speeds are preferred for music and video, and lower speeds for voice.
The data on a magnetic tape can be distorted or erased by external magnetic fields.
Therefore, tapes should be protected from such fields.
Keep magnetic tape away from magnets.
Extreme heat can also result in loss of data, and possibly even physical damage to the tape.
Magnetic disk
The age of the personal computer has seen the development of ever-more-compact data-storage systems.
One of the most versatile is the magnetic disk.
A magnetic disk can be either rigid or flexible. Disks are available in various sizes.
Hard disks store the most data, and are generally found inside of computer units.
Floppy disks or diskettes are usually either 31/2 or 51/4 inch in diameter, and can be inserted
and removed from recording/playback machines called disk drives.
working Principle of Magnetic Disk
The principle of the magnetic disk, on the micro scale, is the same as that of the magnetic tape. The information is stored in digital form; that is, there are only two different
ways that the particles are magnetized. This results in almost perfect, error-free
storage.
On a larger scale, the disk works differently than the tape, simply because of the
difference in geometry.
On a tape, the information is spread out over a long span, and some bits of data are far away from others.
But on a disk, no two bits are ever farther apart than the diameter of the disk. This means that data can be stored and retrieved much more quickly onto, or from, a disk than is possible with a tape.
A typical diskette can store an amount of digital information equivalent to a short novel.
The same precautions should be observed when handling and storing magnetic disks, as are necessary with magnetic tape.
Magnetic bubble memory
Bubble memory is a sophisticated method of storing data that gets rid of the need for
moving parts such as are required in tape machines and disk drives. This type of memory
is used in large computer systems, because it allows the storage, retrieval, and
transfer of great quantities of data. The bits of data are stored as tiny magnetic fields, in
a medium that is made from magnetic film and semiconductor materials.
Books on Magnetic Bubble Memory
Handbook of Semiconductor and Bubble Memories
Magnetic Bubble Memory Technology (Electrical Engineering & Electronics)
Bubble memory makes use of all the advantages of magnetic data storage, as well as the favorable aspects of electronic data storage.
Advantages of electronic memory include rapid storage and recovery, and high density (a
lot of data can be put in a tiny volume of space).
The advantages of magnetic memory include nonvolatility (it can be stored for a long time without needing a constant current source), high density and comparatively low cost.
Read More on Magnetism Topics
- Magnetism-Methods of Magnetization
- MCQ’s on Permeability|Absolute and Relative Permeability
- Magnetic materials: Dia, Para,Ferro,Ferri and Antiferro magnetic materials
- KSEB Sub Engineer Electrical Syllabus-based Study Notes|Sub Engineer Electrical Study materials
Download & Install EEE Made Easy App
Latest Posts in EEE Made Easy
- Environment MCQ for RRB JE CBT 2|Objective Questions Environment for Competitive Exams
- RRB JE CBT 2 Computer Awareness Book Arihant|Objective Computer Awareness Book 2025
- RRB JE CBT 2 Exam Date 2025 Postponed|RRB JE CBT 2 Exam Date
- [PDF]RRB JE Result 03/2024 Cut off, Selected no of candidates for all regions
- [PDF]Final Answer Key Junior Instructor Mechanic Agricultural Machinery|643/2023 Solved Question paper
- Acoustics MCQs|Industries Extension officer|IEO 2025
- LASER MCQs| Industries Extension officer|IEO 2025




