Magnetism-Method of Magnetization
Electromagnetism: Electricity and magnetism
An Electric charge in motion (ie electric current) produces a magnetic field.
Magnets:
A body that can attract the pieces of iron is known as a magnet and the property of a body by virtue of which this attraction takes place is known as magnetism.
Or a body which possess magnetic properties is called a magnet.
Magnetism is one of natures different forms of energy.
A magnet when tied independently hanging with a thread, it will settle in Earth’s geographical North-South directions.
Classification of Magnets:
Magnets can be generally classified in to two:
- Natural magnet
- Artificial Magnet
1.Natural Magnet:
- This type of magnet is irregular in shape and is having very weak magnetic properties.
- Some examples are stones like loadstone and magnetite
2.Artificial Magnet:
- The magnets which are formed by magnetic materials or by the artificial process are called artificial magnets.
- They can be made in a variety of shapes and sizes
There are two types of artificial magnets namely :
- Permanent Magnets 2) Electromagnets
1.Permanent magnets:
- Permanent magnets retain their magnetism even after the magnetizing force is removed. So the magnetic properties are retained for a long time.
- These are made from special steel, hardened steel and alloys like carbon steel, cobalt steel, alnico, alconex, etc.
- Permanent magnets are used in some measuring instruments, dynamo, to collect small iron pieces, headphones, loudspeakers, magnetic needles, etc.
2.Electromagnet:
- An electromagnet is a temporary magnet in which the magnetic properties are retained until the current flow through the coil/ wire which is wound over the magnetic material.
- Normally done by winding a coil of copper, aluminum enameled wire over a soft iron or silicon steel core.
- Used to make electric bells, magnetic crane, electric motors, electric generators, etc.
Magnetic Induction:
Magnetic Induction is the phenomenon by which a magnetic material becomes a magnet when it is placed near a magnet.
A magnet has some distinctive properties:
- Attraction and repulsion of magnetic substances and other magnets
- The two ends of a magnet are called North (N) and South (S) poles
- A magnet will point towards North and South when freely suspended in the air.
- A single-pole magnet does not exist. If a magnet is cut in to small pieces, then each piece will also has two poles.
- The pole strength at two poles of a magnet is same.
- Like poles ( N-N or S-S) of magnets repel each other while unlike poles attract each other.
Method of Magnetization
There are mainly 3 types of magnetization.
- Single Touch method
- Divided Touch Method
- Double Touch Method
1. Single touch Method
In this method, the magnetic material (Iron, nickel, cobalt etc) is magnetized by touching the single-pole a magnet over it. Refer the diagram given below.
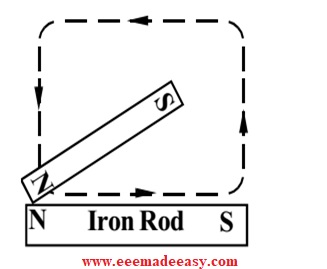
- Consider the Iron bar to be magnetized. Keep the iron bar on a wooden surface.
- Bring any one pole ( North pole as in fig), of a strong magnet to one end of the Iron bar.
- Gently rub the Iron bar from one end to other end. As the other end is reached, the magnet is lifted up and again bring to the other end. See the arrow direction in the fig.
- In this case , the starting end will become North (N) pole and the other end will be South (S) pole.
- If we used the South pole of the magnet to rub on the Iron bar, the starting end will become South (S) pole and other end will become North(N) Pole.
2. Divided Touch Method:
Consider the fig. given below which will illustrate the Divided touch method of magnetization.
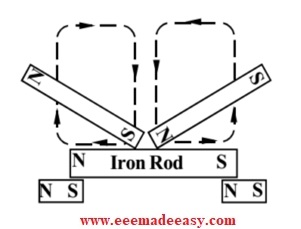
- Here, the Iron bar which is to be magnetized is kept on the top of two permanent magnets. These supporting magnets will help to increase the magnetization also.
- In the divided touch method, two strong permanent magnets will be taken .
- With their opposite poles kept at the middle of the rod, gently rub on the Iron rod till the end. As the magnets reach the end, lift them up and repeat the procedure several times.
- From the fig. you can see that the end where the North pole of Permanent magnet leaves will become the South pole and the end where the South pole of the other permanent magnet leaves will become the South Pole.
3. Double Touch Method:
Consider the arrangement shown in the fig. below.
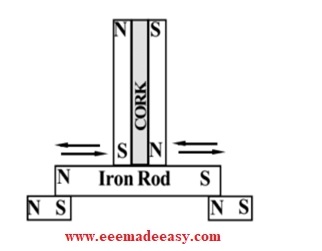
- In the Double touch method also we will make use of two permanent magnets on the top of the Iron bar to be magnetized.
- These permanent magnets are held together such that their opposite poles are together, and in between the two magnets there is a piece of wood or cork.
- This combination is placed at the centre on the Iron bar and moved them to and fro with out lifting it.
- The Iron bar become a magnet such that, the each end become the opposite pole of the nearest stroking magnet.
- The supporting magnets supports the magnetization. Note the polarity of supporting magnets also in the fig.
This is how a magnetic material can be magnetized and transformed as magnet.
There are Some other terms related to Magnetism:
Magnetic Materials: Dia,Para,Ferro, Ferri etc
Magnetic Materials: Dia,Para,Ferro, Ferri etc
You can read each in the following posts.
- Magnetic Materials
- Magnetic field and magnetic lines of force
- Magnetic Flux and Magnetic flux density
- Permeablity of a magnetic material
- Magneto motive force (m.m.f)
- Magnetic field Intensity
- Intensity of Magnetization
- Reluctance, Permeance
- Magnetization Curve
- Magnetic Hysterisis
- Magnetic Circuits
- Environment MCQ for RRB JE CBT 2|Objective Questions Environment for Competitive Exams
- RRB JE CBT 2 Computer Awareness Book Arihant|Objective Computer Awareness Book 2025
- RRB JE CBT 2 Exam Date 2025 Postponed|RRB JE CBT 2 Exam Date
- [PDF]RRB JE Result 03/2024 Cut off, Selected no of candidates for all regions
- [PDF]Final Answer Key Junior Instructor Mechanic Agricultural Machinery|643/2023 Solved Question paper
- Acoustics MCQs|Industries Extension officer|IEO 2025
- LASER MCQs| Industries Extension officer|IEO 2025
- Practical Types of Capacitors
- [PDF] Syllabus JUNIOR INSTRUCTOR MECHANIC AGRICULTURAL MACHINERY|643/2023 Syllabus Kerala PSC
- [PDF] Syllabus JUNIOR INSTRUCTOR WOOD WORK TECHNICIAN|674/2023 Syllabus Kerala PSC
1 thought on “Magnetism-Methods of Magnetization”