What is an Electrical distribution system?
The electrical system, which distributes electrical energy to the consumers, is known as a distribution system.
The electrical system between the substations and service mains is known as a distribution system.
Download & Install EEE Made Easy App
There are two types of distribution systems: primary and secondary distributions.
The power, which is received at 33 kV, 66 kV or 110 kV, is stepped down to 11 kV, where the power is distributed along main roads and is called the primary distribution system.
The power is distributed through distribution lines called distributors, which run along the streets of consumers.
The distribution lines, which feed the power from primary distribution to the distributor, are called feeders.
The power is then distributed to the consumers from the distributors using service lines.
Therefore, feeders, along with service lines, make up the secondary distribution system.
Essential Components of Transmission and Distribution Systems
Both transmission and distribution of electrical energy from generating stations to consumers can be done using overhead lines or underground cables.
Components of Overhead Lines
The essential components of overhead lines, which can be used for transmitting or distributing electrical energy are:
- Conductors, which are used to carry electrical power from the sending-end to the receiving-end of a particular station.
- Support, which is provided using poles or towers, helps in keeping the conductors at a suitable height from the ground.
- Insulators, which are used to insulate the conductors from the ground.
- Cross-arms are used to provide support to the insulators.
- Miscellaneous items like lightning arrestors, phase plates and so on.
Components of Underground Cables
Schematic Diagram of an Underground able
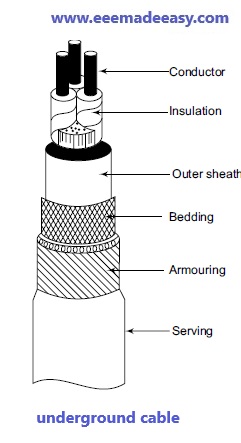
The essential components of underground cables are shown in Figure which can be used for transmitting or distributing electrical energy.
The various components of the cables are explained as follows:
- Cores or conductors, which are made up of stranded tinned copper or aluminium to provide flexibility to the cable.
- Insulation is a layer, which is placed above the conductor, with a suitable thickness that decides the maximum voltage that can be transmitted through the cable.
- Metallic sheath is provided in the cable to protect the cable from moisture, gases or other liquids, which could damage the cable.
- Bedding, which is made up of fibrous material like jute or hessian tape, is provided over the metallic sheath to prevent it from corrosion and other mechanical injuries.
- Armouring, which is made up of galvanized steel wire or steel tape, to protect the cable while it is being laid or handled.
- Serving is used for protecting the armouring from atmospheric conditions and is made up of a fibrous material called jute.
Comparison Between Overhead Lines and Underground Cables
Even though the electrical energy can be transmitted or distributed using overhead lines and underground cables, the selection of one over the other is based on the following reasons listed in Table below.
Overhead Lines Vs Underground Cables
| Parameter | Overhead Lines | Underground Cables |
|---|---|---|
| Public safety | More dangerous to the public | Less hazardous to the public |
| Initial cost | Less costly | It is 10 times the cost of an overhead line |
| Flexibility | More flexible and can be modified easily | Less flexible |
| Faults | Chance of fault occurrence is more | Less chance of fault occurrence |
| Appearance | Bad, since the wiring is visible | Good, since the wiring is not visible |
| Fault location and repair | Easier to locate the fault and repair it | Difficult to locate the fault and repair it |
| Useful life | Less | More |
| Maintenance cost | High | Very low |
| Interference with communication circuits | Faces problems due to interference | No interference with the communication circuits |
| Lightning | Liable to hazards from lightning | Not liable to hazards from lightning |
| Submarine crossings | Cannot be used | Can be used |
| Transmission | Used for long-distance transmission | Used for short-distance transmission |
Read more on Power System
- Electrical Power System Problems and Solutions
- Three Phase System|Advantages of Three Phase System
- [MCQ Set 3]Electrical Power Generation, Transmission and Distribution MCQ Questions
- Electrical power Generation
- Wind Energy Power Plants|Wind Power Generation|Wind Mill Working
- Transmission tower design|Electrical tower design
- Types of Transmission Towers|Electrical Tower Types
- Transmission structures|Transmission towers and Transmission Poles|Electric Tower
- Parts of a Power transmission line and Transmission tower|Transmission tower parts
- Steam power plant Layout|General layout of Steam Power Station
- Lightning Arrester|ESE Lightning Arrester & Conventional Iightning Arrester
- [MCQ Set 2]Electrical Power Generation, Transmission and Distribution MCQ Questions
- [MCQ Set 1]Electrical Power Generation, Transmission and Distribution MCQ Questions
- Electrical power Generation
- Steam power plants|Steam power generator Plant|Thermal Power Plants
- Comparison of ac and dc transmission
- Types of Insulators in Transmission lines
- Skin Effect and Proximity Effect
- Electrical Distribution System
Join EEE Made Easy Telegram channel
Latest Posts EEE Made Easy
Latest Posts in EEE Made Easy
- Environment MCQ for RRB JE CBT 2|Objective Questions Environment for Competitive Exams
- RRB JE CBT 2 Computer Awareness Book Arihant|Objective Computer Awareness Book 2025
- RRB JE CBT 2 Exam Date 2025 Postponed|RRB JE CBT 2 Exam Date
- [PDF]RRB JE Result 03/2024 Cut off, Selected no of candidates for all regions
- [PDF]Final Answer Key Junior Instructor Mechanic Agricultural Machinery|643/2023 Solved Question paper
- Acoustics MCQs|Industries Extension officer|IEO 2025
- LASER MCQs| Industries Extension officer|IEO 2025




