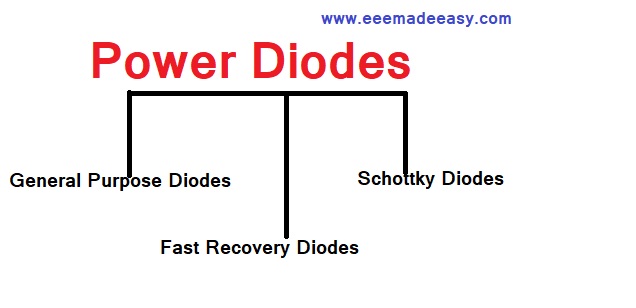
Types of power Diodes
Power diodes can be classified as
- General purpose diodes.
- High speed (fast recovery) diodes.
- Schottky diode.
Books for Power Electronics
- Power Electronics: Devices, Circuits and Applications, by Muhammad H. Rashid
- Power Electronics, by P.S. Bimbhra
- Power Electronics, by M Singh & K Khanchandani
General Purpose Diodes
The diodes have high reverse recovery time of about 25 microsecs ( sec).
They are used in low speed (frequency) applications. e.g., line commutated converters, diode rectifiers and converters for a low input frequency upto 1 KHz.
Diode ratings cover a very wide range with current ratings less than 1 A to several thousand amps (2000 A) and with voltage ratings from 50 V to 5 KV.
These diodes are generally manufactured by diffusion process.
Alloyed type rectifier diodes are used in welding power supplies.
They are most cost-effective and rugged and their ratings can go upto 300A and 1KV.
Fast Recovery Diodes
The diodes have low recovery time, generally less than 5 s. The major field of applications is in electrical power conversion i.e., in free-wheeling ac-dc and dc-ac converter circuits.
Their current ratings is from less than 1 A to hundreds of amperes with voltage ratings from 50 V to about 3 KV.
The use of fast recovery diodes are preferable for free-wheeling in SCR circuits because of low recovery loss, lower junction temperature and reduced di /dt .
For high voltage ratings greater than 400 V they are manufactured by diffusion process and
the recovery time is controlled by platinum or gold diffusion.
For less than 400 V rating epitaxial diodes provide faster switching speeds than diffused diodes. Epitaxial diodes have a very narrow base width resulting in a fast recovery time of about 50 ns.
Schottky Diodes
A Schottky diode has a metal (aluminum) and semi-conductor junction.
A layer of metal is deposited on a thin epitaxial layer of the n-type silicon.
In the Schottky diode, there is a larger barrier for electron flow from metal to semi-conductor.
The figure shows the Schottky diode.
When the Schottky diode is forward biased free electrons on the n-side gain enough energy to flow into the metal causing forward current.
Since the metal does not have any holes there is no charge storage, decreasing the recovery time. Therefore a Schottky diode can switch off faster than an ordinary p-n junction diode.
A Schottky diode has relatively low forward voltage drop and reverse recovery losses.
The leakage current is higher than a p-n junction diode.
The maximum allowable voltage is about 100 V. Current ratings vary from about 1 to 300 A.
They are mostly used in low voltage and high current dc power supplies.
The operating frequency may be as high as 100-300 kHz as the device is suitable for high-frequency
application.
Comparison Between Different Types Of Diodes
| General Purpose Diodes | Fast Recovery Diodes | Schottky Diodes |
|---|---|---|
| Upto 5000V & 3500A | Upto 3000V and 1000A | Upto 100V and 300A |
| Reverse recovery time – High | Reverse recovery time – Low | Reverse recovery time – Extremely low. |
| t rr = 25 Micro Sec | t rr = 0.1- 5 Micro Sec | t rr = a few nano seconds |
| Turn off time – High | Turn off time – Low | Turn off time – Extremely low |
| Switching frequency – Low | Switching frequency – High | Switching frequency – Very high. |
| V = 0.7V to 1.2V | V = 0.8V to 1.5V | V 0.4V to 0.6V |
- [PDF]Assistant Engineer Electronics PWD Syllabus|071/2024 syllabus Kerala PSC
- Environment MCQ for RRB JE CBT 2|Objective Questions Environment for Competitive Exams
- RRB JE CBT 2 Computer Awareness Book Arihant|Objective Computer Awareness Book 2025
- RRB JE CBT 2 Exam Date 2025 Postponed|RRB JE CBT 2 Exam Date
- [PDF]RRB JE Result 03/2024 Cut off, Selected no of candidates for all regions
- [PDF]Final Answer Key Junior Instructor Mechanic Agricultural Machinery|643/2023 Solved Question paper
- Acoustics MCQs|Industries Extension officer|IEO 2025
- LASER MCQs| Industries Extension officer|IEO 2025
- Practical Types of Capacitors
- [PDF] Syllabus JUNIOR INSTRUCTOR MECHANIC AGRICULTURAL MACHINERY|643/2023 Syllabus Kerala PSC
- [PDF] Syllabus JUNIOR INSTRUCTOR WOOD WORK TECHNICIAN|674/2023 Syllabus Kerala PSC
- [PDF] Syllabus JUNIOR INSTRUCTOR MECHANIC CONSUMER ELECTRONIC APPLIANCES|670/2023 Syllabus Kerala PSC