Practical Types of Capacitors : Practical types of capacitors are characterized by the material used for their dielectric. The main types include: variable air, mica, paper, ceramic, plastic, titanium oxide, and electrolytic.
Practical Types of Capacitors
1. Variable air capacitors.
These usually consist of two sets of metal plates (such as aluminum) one fixed, the other variable. The set of moving plates rotate on a spindle as shown by the end view of Figure
As the moving plates are rotated through half a revolution, the meshing, and therefore the capacitance, varies from a minimum to a maximum value. Variable air capacitors are used in radio and electronic circuits where very low losses are required, or where a variable capacitance is needed. The maximum value of such capacitors is between 500 pF and 1000 pF.
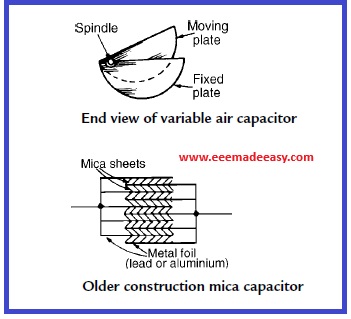
2. Mica capacitors.
A typical older type construction is shown in Figure Usually the whole capacitor is impregnated with wax and placed in a bakelite case. Mica is easily obtained in thin sheets and is a good insulator. However, mica is expensive and is not used in capacitors above about 0.2 μ F. A modified form of mica capacitor is the silvered mica type. The mica is coated on both
sides with a thin silver layer, forming the plates. Capacitance is stable and less likely to change with age. Such capacitors have a constant capacitance with change of temperature, a high working voltage rating and a long service lifeand are used in high frequency circuits with fixed values of capacitance up toabout 1000 pF.
3. Paper capacitors.
A typical paper capacitor is shown in Figure where the roll’s length corresponds to the required capacitance. The whole is usually impregnated with oil or wax to exclude moisture and then placed in a plastic or aluminum container for protection. Paper capacitors are made in various working voltages up to about 150 kV and are used where loss is not very important. The maximum value of this type of capacitor is between 500 pF and 10 μ F. Disadvantages of paper capacitors include variation in capacitance with temperature change and a shorter service life than most other types of capacitors.
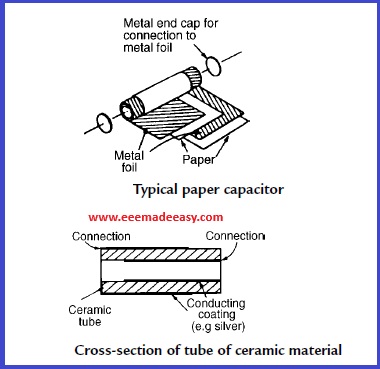
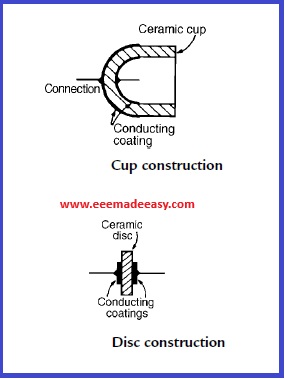
4. Ceramic capacitors .
These are made in various forms, each type of construction depending on the value of capacitance required. For high values, a tube of ceramic material is used as shown in the cross-section of Figure. For smaller values the cup construction is used as shown in Figure, and for still smaller values the disc construction shown in Figure is used. Certain ceramic materials have a very high permittivity and this enables capacitors of high capacitance to be made which are of small physical size with a high working voltage rating. Ceramic capacitors are available in the range 1 pF to0.1 μ F and may be used in high-frequency electronic circuits subject to a wider range of temperatures.
5. Plastic capacitors
Some plastic materials such as polystyrene and Tefl on canbe used as dielectrics. Construction is similar to the paper capacitor but using aplastic film instead of paper. Plastic capacitors operate well under conditions ofhigh temperature, provide a precise value of capacitance, a very long service lifeand high reliability.
6. Titanium oxide capacitors
have a very high capacitance with a small physical size when used at a low temperature.
7. Electrolytic capacitors
Construction is similar to the paper capacitor with aluminum foil used for the plates and with a thick absorbent material, such as paper, impregnated with an electrolyte (ammonium borate), separating theplates.
The finished capacitor is usually assembled in an aluminum container and hermetically sealed. Its operation depends on the formation of a thin aluminum oxide layer on the positive plate by electrolytic action when a suitable direct potential is maintained between the plates.
This oxide layer is very thin and forms the dielectric. (The absorbent paper between the plates is a conductor and does not act as a dielectric.) Such capacitors must always be used on DC and must be connected with the correct polarity; if this is not done the capacitor will be destroyed since the oxide layer will be destroyed. Electrolytic capacitors are manufactured with working voltage from 6 V to 600 V, although accuracy is generally not very high.
These capacitors possess a much larger capacitance than other types of capacitors of similar dimensions due to the oxide film being only a few microns thick. The fact that they can be used only on DC supplies limit their usefulness.
Join EEE Made Easy Whatsapp Channel
Join EEE Made Easy Telegram channel
Download & Install EEE Made Easy App
Download EEE Made Easy Ebook PDF Free
Latest Posts in EEE Made Easy
- Environment MCQ for RRB JE CBT 2|Objective Questions Environment for Competitive Exams
- RRB JE CBT 2 Computer Awareness Book Arihant|Objective Computer Awareness Book 2025
- RRB JE CBT 2 Exam Date 2025 Postponed|RRB JE CBT 2 Exam Date
- [PDF]RRB JE Result 03/2024 Cut off, Selected no of candidates for all regions
- [PDF]Final Answer Key Junior Instructor Mechanic Agricultural Machinery|643/2023 Solved Question paper
- Acoustics MCQs|Industries Extension officer|IEO 2025
- LASER MCQs| Industries Extension officer|IEO 2025



