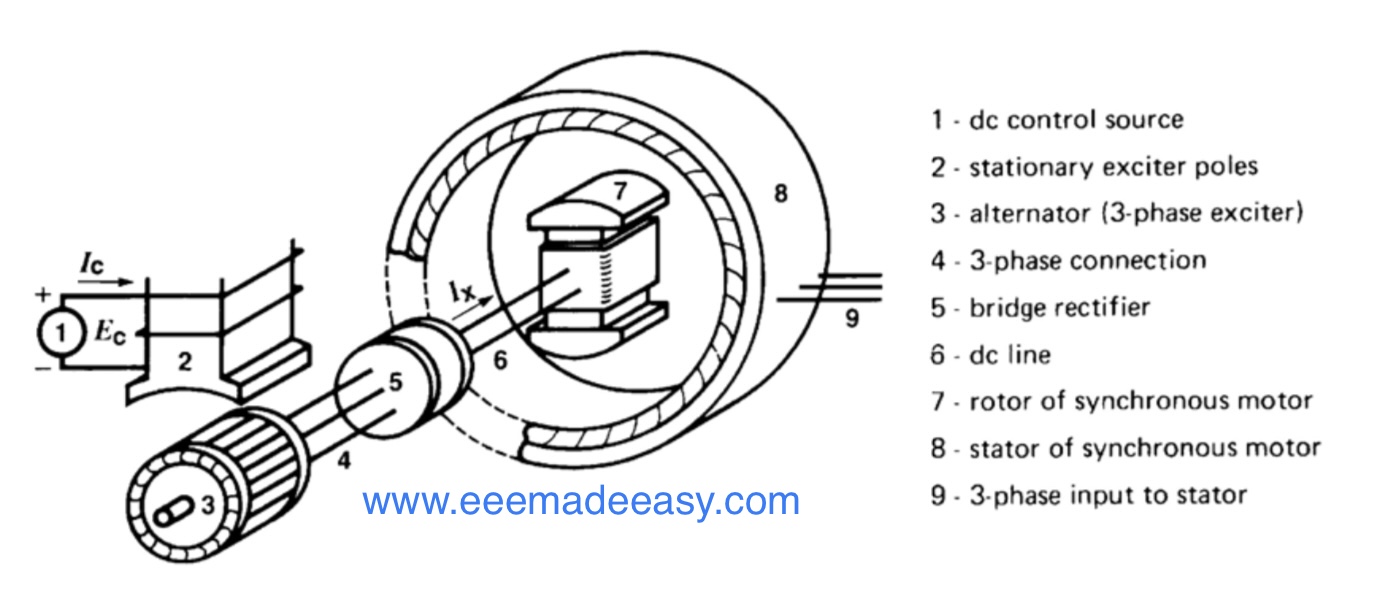
Synchronous Machines: Synchronous Motors and Synchronous generators (Alternators). A synchronous generator is an electrical machine producing alternating emf (Electromotive force or voltage) of constant frequency. A synchronous motor is the same physical machine as a generator, except that the direction of real power flow is reversed.
synchronous motor
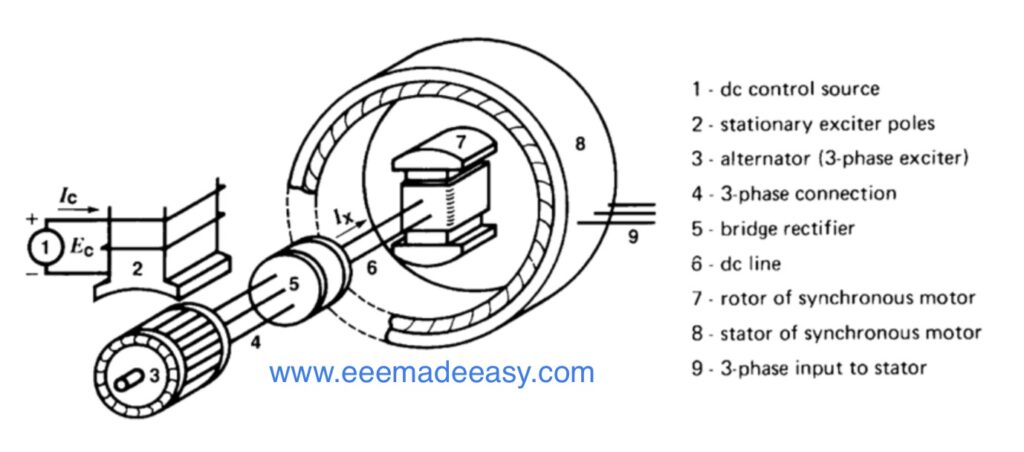
A synchronous motor is the same physical machine as a generator, except that the direction of real power flow is reversed.
- When operating as motors (by connecting them to a 3-phase source), they are called synchronous motors.
- Synchronous motors are used to convert AC electric power to mechanical power at constant speed called as Synchronous Speed.
- Synchronous motors run in synchronism with the revolving field.
- The speed of rotation is tied to the frequency of the source.
- The motor speed stays constant, irrespective of the load or voltage of the 3-phase line and it does not depend on the torque acting on it.
- So it has a constant-speed torque characteristic.
- The efficiency of synchronous motor is around 90%–93%.
Synchronous generator
A synchronous generator is an electrical machine producing alternating emf (Elec- tromotive force or voltage) of constant frequency.
In our country the standard commercial frequency of AC supply is 50 Hz. In U.S.A. and a few other countries the frequency is 60 Hz. The AC voltages generated may be single phase or 3-phase depending on the power supplied.
For low power applications single phase generators are preferable. The basic prin- ciples involved in the production of emf and the construction details of the generators are discussed below.
Electrical Degree and Mechanical degree in Synchronous machines
Generation of emf in Synchronous machines
In 1831 Faraday discovered that an emf can be induced (or generated) due to relative motion between a magnetic field and a conductor of electricity.
This voltage was termed as the induced emf since the emf is produced only due to motion between the conductor and the magnetic field without actual physical contact between them.

The principle of electromagnetic induction
The magnetic field is produced by the two fixed poles one being the north pole from which the magnetic flux lines emerge and enter into the other pole known as the south pole.
It was found that the magnitude of the voltage induced in the conductor is proportional to the rate of change of flux lines linking the conductor.
Importance of Electrical Machines
With the development of the technology and the way in which human labour is getting minimized and the comforts increasing tremendously the use of electrical energy is ever increasing.
Basically electric power is the main source of energy for carrying out many functions, as it is a clean and efficient energy source, which can be easily transmitted over long distances.
With the availability of Transformer for changing the voltage levels to a very high value (of say 132kV to 400kV) the use of AC power has increased rapidly and the DC power is used only at remote places where AC power cannot be supplied through power lines or cables or for a few social purposes.
- Read Here Synchronous machines notes and MCQs
- Read about Synchronous Machines
- Construction of Synchronous Machines
- Read Here Electrical and Mechanical Degrees in Synchronous Machines
- Synchronous Machines Advantages and disadvantages
- Parallel operations of Alternators
- Synchronous machines MCQ 3
- Synchronous machines MCQ 2
- Synchronous machines MCQ 1
- Single phase alternator|Synchronous Generator
- Three-phase alternator|3 phase Synchronous Generator
Electrical Machines Best Books
| Sl no. | Book Title | Author | Buy Link |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Textbook Of Electrical Technology : Ac And Dc Machines (volume – 2) | B L Theraja, AK Theraja | check price |
| 2 | Theory & Performance of Electrical Machines | J.B. Gupta | check price |
| 3 | Electrical Machines | by V.K Mehta, Rohit Mehta | check price |
| 4 | Electric Machines | PS Bimbhra | check price |
| 5 | Electrical Machines | S.K. Bhattacharya | check price |