Thermoelectric transducer: A temperature transducer, that converts thermal energy into electrical energy, is known as a thermoelectric transducer. A thermocouple is the most commonly used thermoelectric transducer.
What is a Thermocouple?
Thermocouple, a type of primary transducer, is used for measuring temperature, where the change in temperature arising from two dissimilar metals is converted into electrical energy.
Thermoelectric phenomena like Seebeck, Peltier, and Thompson effects are used to describe the thermocouple behavior.
Seebeck Effect
Seebeck Effect was introduced by Prof. Seebeck in 1821, which states that if two wires of different metals,
like copper and iron, are joined together to form a closed circuit with two junctions and if those junctions
are maintained at different temperatures, then an electric current will flow through the closed circuit i.e.,
the current will flow from copper to iron in the hot junction and from iron to copper in the cold junction.
The explanation of Seebeck effect is shown in Figure below.
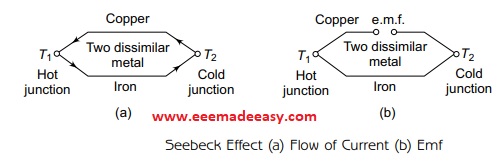
In addition, it also says that an emf called Seebeck emf, which is directly proportional to the change in temperature appears across the open circuit if the copper wire is cut at a particular point
Read Also: Thermistor| What is a Thermistor
Peltier Effect
Professor Peltier introduced this effect, which is a reverse of Seebeck effect, in 1824. It states that if two wires of dissimilar metals form two junctions when an external voltage source is connected, as shown in Figure below, then the current starts flowing through both the junctions.
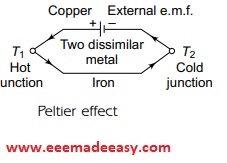
It also states that the heat is absorbed at a junction where the current is flowing from copper to iron, making the junction T1 hot, and heat is liberated at a junction where the current is flowing from iron to copper,
making the junction T2 cold.
Thompson Effect
It is a reversible heat flow effect, which was introduced by Professor Thompson.
Thompson Effect states that when a current flows through the copper conductor with a thermal gradient along its length, then heat is released at a junction where the current and heat flow are in the same direction and heat is absorbed at a junction where different directions exist for current and heat flow
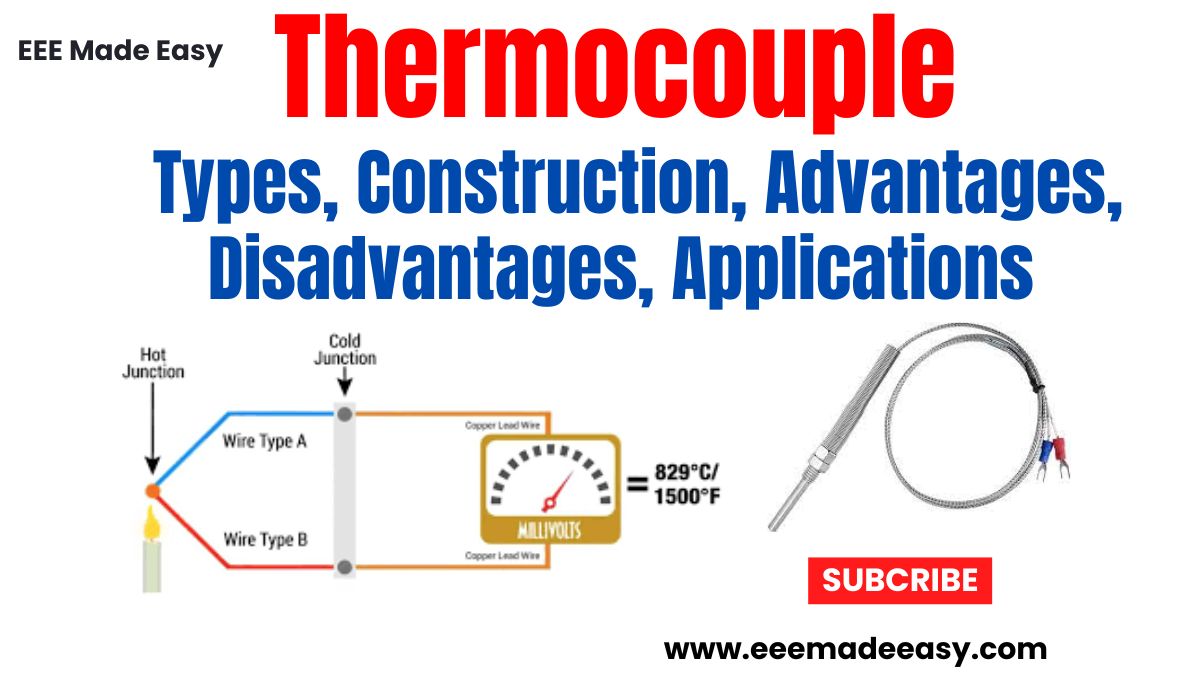
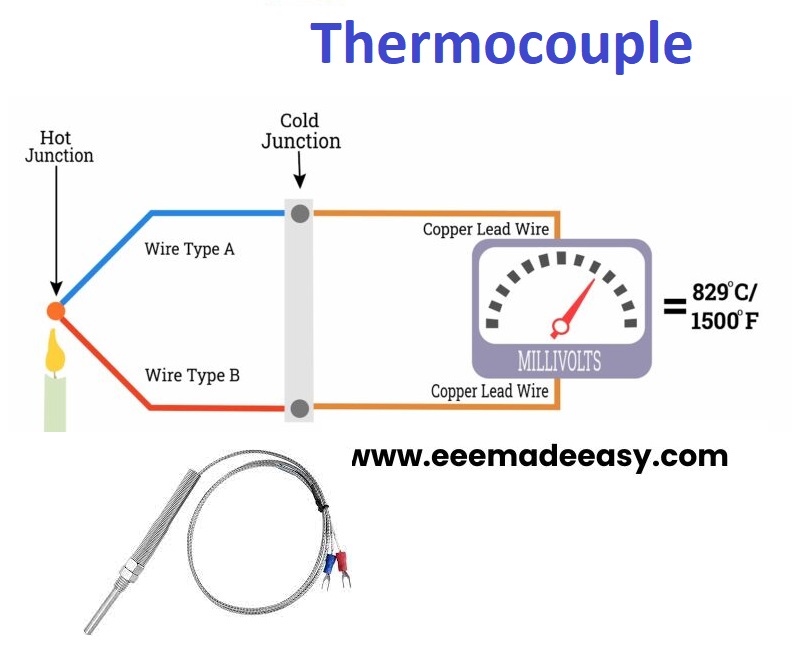
Construction of a Thermocouple
Two dissimilar metals, when joined together to form two junctions T1 and T2, form a thermocouple, as shown in Figure .
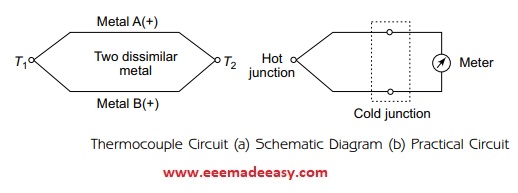
Usually, T2 is kept at constant reference temperature and is referred as cold junction or reference junction. The temperature which is to be measured is subjected to T1 and hence it is referred as hot junction or measuring junction.
When there is a temperature difference between T1 and T2, an emf that is proportional to the temperature gradient gets generated and can be measured using any meter or recorder, as shown Figure (b)
Generally, the junction in the thermocouple is formed in two ways: twisted weld and butt weld.
In twisted weld, two large sized wires are twisted and welded together with several turns to give mechanical strength, while in butt weld, two comparatively small wires are fused together into a round bend.
The normal sizes of metals are: 0.5 mm diameter for noble metals and 1.5 to 3 mm diameter for base metals.
Types of Thermocouples
Based on the materials used in the thermocouple and the range of temperature it can measure, there are
different types of thermocouples listed in Table.
Type of Thermocouples
| Type of Thermocouples | Material Used | Temperature Range |
|---|---|---|
| T | Copper – constantan | -250°C to 400°C |
| J | Iron – constantan | –200°C to 850°C |
| K | Chromel – Alumel | –200°C to 110°C |
| E | Chromel – Constantan | –200°C to 850°C |
| S | Platinum – Platinum rhodium | 0°C to 1400°C |
| — | Tungsten – molybdenum | 0°C to 2700°C |
| — | Tungsten-Rhenium | 0°C to 2600° |
Advantages, Disadvantages, and Applications of Thermocouples
Here listed the Advantages, Disadvantages, and Applications of Thermocouples.
Advantages of Thermocouples
- Rugged construction
- Covers wide range of temperature: –270°C to 2700°C
- Most suitable for temperature measurement in industrial furnaces
- Cheaper in cost
- Easy to check the calibration
- Offers good reproducibility
- High response speed and good accuracy
Disadvantages of Thermocouples
- To have high accuracy, it is necessary to have cold junction compensation.
- Non-linear characteristics exist between induced emf and temperature.
- Possible to have stray voltage pickup.
- Signal amplification is required for many applications.
Applications of Thermocouples
- Testing temperatures associated with different process plants e.g. chemical production, petroleum
refineries, heating appliance safety, food industries, steel, iron and aluminium industries, plastics and
resin industries. - Suitable for low temperature and cryogenic applications.
- Temperature profiling in ovens, furnaces and kilns.
- Temperature measurement of gas turbine and engine exhausts.
Read More
- Thermistor| What is a Thermistor
- RTD vs Thermistor|Comparison between RTD and Thermistor
- Transducer Types, Parts, Working, Applications with Examples
Measurements & Instruments Study Notes
- [PDF]Electrical Measurements Measuring Instruments Study Notes PDF|EMMI Notes EEE Made Easy
- MCQ on Electrical Instruments
- Types of Errors in Instruments| Instrument Errors
- MCQ’s on Electrical Measuring Instruments|Instruments Objective Questions
- Electrical measuring instruments|Types of Measuring Instruments
- Static characteristics of instruments
- Types of measuring instruments- www.eeemadeeasy.com
- Moving Iron Instruments
- Instruments- Basics
- PMMC Instruments
- Types of instruments
- Essentials of Indicating instruments
- MCQ’s on Galvanometer|Galavnometer Questions & Answers
- MCQs on potentiometer|potentiometer Questions and answers
- TOD Meter or Time of Day Meter
- Light meters or illumination meter|Lux meter
- VU and decibel meters
- Multimeter- Principle and operation
- Digital readout meters-principle and operation
- Watt-hour meters- principle and operation
- Wattmeter -principle and working
- FET and vacuum-tube voltmeters
- Ohmmeter- basic principle and working
- Ammeters|Current Measurement
- Voltmeter- Principle and operation
- The household energy meter is
- Q Meter
- Thermistor| What is a Thermistor
- RTD vs Thermistor|Comparison between RTD and Thermistor
Latest Posts in EEE Made Easy
- Environment MCQ for RRB JE CBT 2|Objective Questions Environment for Competitive Exams
- RRB JE CBT 2 Computer Awareness Book Arihant|Objective Computer Awareness Book 2025
- RRB JE CBT 2 Exam Date 2025 Postponed|RRB JE CBT 2 Exam Date
- [PDF]RRB JE Result 03/2024 Cut off, Selected no of candidates for all regions
- [PDF]Final Answer Key Junior Instructor Mechanic Agricultural Machinery|643/2023 Solved Question paper
- Acoustics MCQs|Industries Extension officer|IEO 2025
- LASER MCQs| Industries Extension officer|IEO 2025