.
What is a transducer?
The transducer may be defined as any device that convert the energy from one form to another.
What is a transducer used for?
Most of the transducers either convert electrical energy in to mechanical displacement and convert some non electrical physical quantities like temperature, Light, Pressure , Force , Sound etc to an electrical signals.
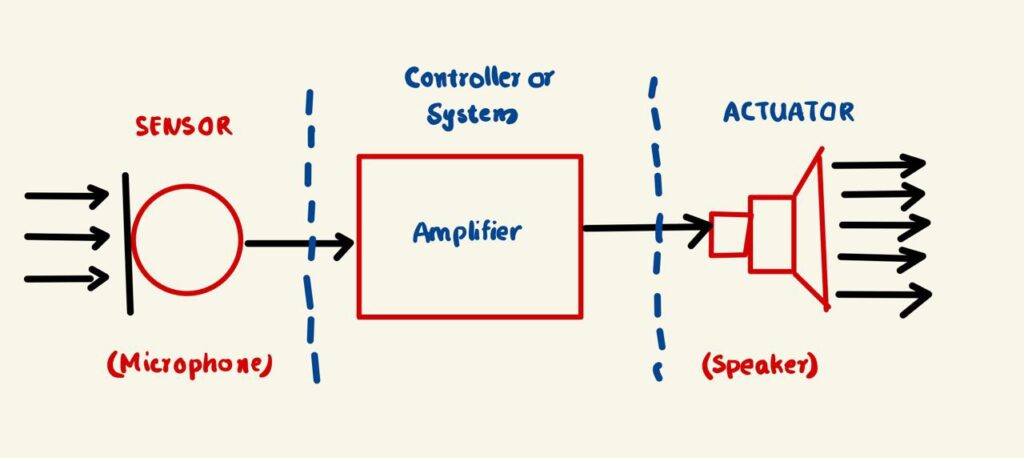
In an electronics instrument system the function of transducers is of two types.
1. To detect or sense the pressure, magnitude and change in physical quantity being measured.
2. To produce a proportional electrical signal.
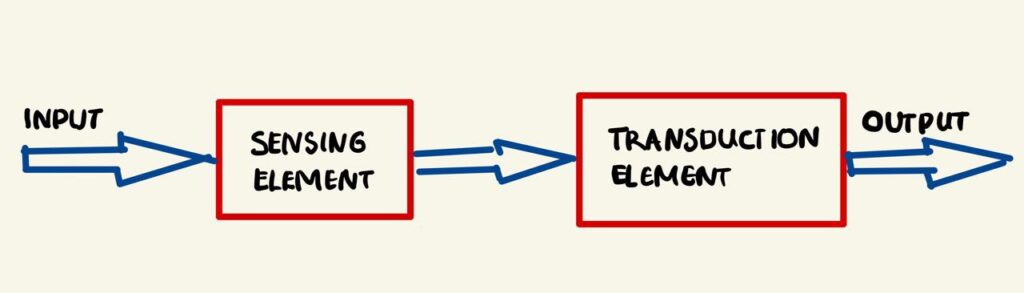
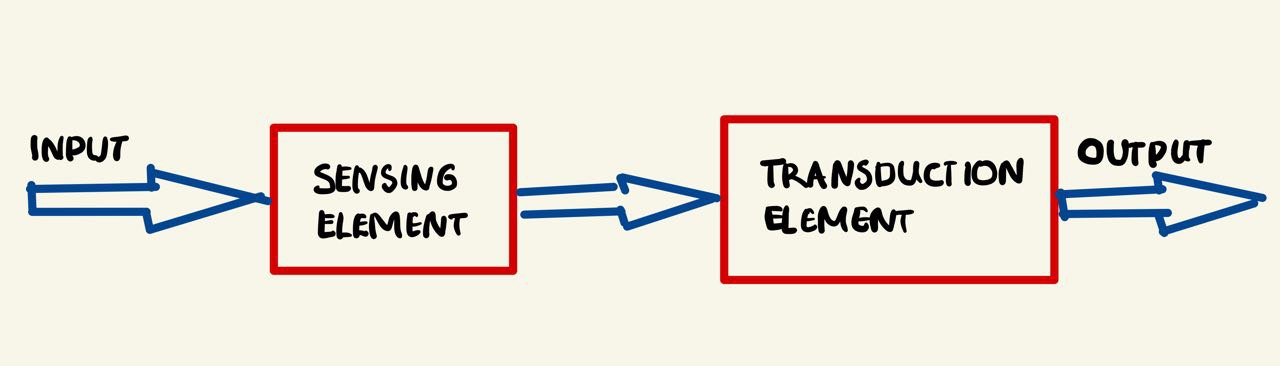
1. Sensing Element
The physical quantity or its rate of change is sensed and responded to by this part of the transistor.
2. Transduction Element
The output of the sensing element is passed on to the transduction element. This element is responsible for converting the non-electrical signal into its proportional electrical signal.
Classification of Transducers
Transducer types
The Classification of Transducers is done in many ways.
Some of the criteria for the classification are based on
- the area of application
- Method of energy conversion
- Nature of output signal
- According to Electrical principles involved
- Electrical parameter used
- principle of operation
- Typical applications.
Classification of Transducer/ types of transducers
- Based upon the transduction principle used
2. Primary & Secondary transducers
3.Active & Passive transducers
4. Analog & Digital transducers
5.Transducers & Inverse transducers
1. Based upon the transduction principle:-
Resistance transducers
Potentimeter devices, Resistance strain gauge, Pirani guage or hot wire meter, Resistance thermometer, Thermister, Resistance hygrometer, Photoconductive cell.
Capacitance transducers
Variable capacitance pressure gauge, Capacitor microphone, Dielectric gauge.
Inductance Transducers
Magnetic circuit transducer, Reluctance pick-up, Differential transformer, Eddy current guage, Magneto striction gauge.
Voltage & Current transducers
Hall effect transducer, Ionisation chamber, Photoemissive cell,Photomultiplier tube.
Self generating transducers
Thermocouple, Thermopile, Moving coil generator, Piezoelectric transducer, Photovoltaic.
2. Primary & Secondary transducers
Some transducers contain mechanical as well as electrical devices
. The mechanical device converts the physical quantity to be measured into a mechanical signal.
Such mechanical devices are called as primary transducers, because they deal with the physical quantity to be measured.
• The electrical device then converts this mechanical signal into a corresponding electrical signal. Such electrical device are known as secondary transducers.
Example of Primary and secondary transducer Primary transducer Displacement voltage Secondary transducer
3. Active & Passive Transducer
Transducers that don’t require an auxiliary power source to produce their output are known as ‘Active transducers’ or self generating type.
eg: Moving coil, Piezoelectric crystal, Thermocouple, Photovoltaic cell.
On the other hand transducer that can’t work on the absence of external power supply are called ‘passive transducers’.
eg: Resistive, Capacitive, Inductive.
4. Analog & Digital transducers
Analoge transducers converts input quantity into an analog output which is continous function of time.
eg: strain gauge, LVDT, Thermocouple. Thermister.
Digital transducer converts input quantity into an electrical output is in the form of pulses
eg: Glass scale, Metallic scale.
5. Transducers & Inverse Transducers
inverse transducers are just the opposite of transducers in function. Inverse transducers converts electrical quantity in non electrical quantity.
Just think about a current coil moving in magnetic field which is an inverse transducer.
eg: Peizoelectrical crystal.
Basically, there are two types of transducers, electrical, and mechanical.
Electrical Transducer
An electrical transducer is a sensing device by which the physical, mechanical or optical quantity to be measured is transformed directly by a suitable mechanism into an electrical voltage/current proportional to the input measurand.
Transducer Properties
An electrical transducer must have the following parameters:
Linearity: The relationship between a physical parameter and the resulting electrical signal must be linear.
Sensitivity: This is defined as the electrical output per unit change in the physical parameter (for example V/°C for a temperature sensor).
High sensitivity is generally desirable for a transducer.
Dynamic Range: The operating range of the transducer should be wide, to permit its use under a wide range of measurement conditions.
Repeatability: The input/output relationship for a transducer should be predictable over a long period of time. This ensures reliability of transducer.
Physical Size: The Electrical Transducer Definition must have minimal weight and volume, so that its presence in the measurement system does not disturb the existing conditions
What is the main difference between sensor and transducer?
Difference Between a Transducer & Sensor
| Transducers | Sensors |
|---|---|
| It converts energy from one form to another. | It senses physical quantities and converts it into a readable form. |
| Eg: Cable extension transducer, linear transducer and microphones | Eg:Thermistors, pressure switches and motion sensors |
- Environment MCQ for RRB JE CBT 2|Objective Questions Environment for Competitive Exams
- RRB JE CBT 2 Computer Awareness Book Arihant|Objective Computer Awareness Book 2025
- RRB JE CBT 2 Exam Date 2025 Postponed|RRB JE CBT 2 Exam Date
- [PDF]RRB JE Result 03/2024 Cut off, Selected no of candidates for all regions
- [PDF]Final Answer Key Junior Instructor Mechanic Agricultural Machinery|643/2023 Solved Question paper