What is Ohm’s Law? Ohm’s Law Statement Formula & Examples
ohms law statement
What is Ohm’s Law?
Ohm’s Law applies to electric conduction through good conductors.
Ohm’s law solved Problems|Problems based on ohm’s law
Ohms Law Statement:
Ohms law can be stated as, the ratio of potential difference (V) between any two points on a conductor to the current (I) flowing between them, is constant, provided the temperature of the conductor does not change.
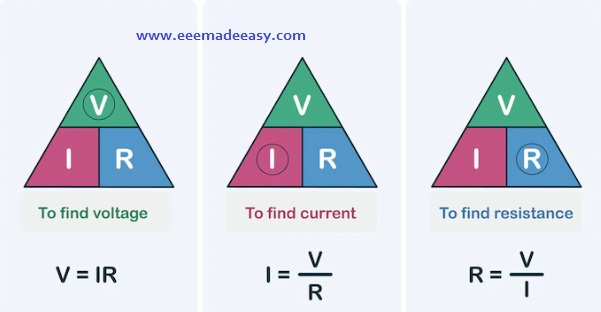
Ohm’s Law Formula:
In other words, V/I= constant
or V/I= R
where R is the resistance of the conductor between the two points considered.
Put in another way, it simply means that provided R is kept constant, current is directly proportional to the potential difference across the ends of a conductor.
However, this linear relationship between V and I does not apply to all non-metallic conductors.
For example, for silicon carbide, the relationship is given by V = KI mwhere K and m are constants and m is less than unity.
Ohm’s Law also does not apply to non-linear devices such as Zener diodes and voltage-regulator (VR) tubes.
Also Read
- Electric current, Voltage, Resistance- Definition, and units
- Laws of resistance- Sp: resistance inductance and Conductivity, Effect of temperature on resistance- Temp. coefficient.
- D. C. Circuits- Ohm’s law
- series, parallel, series-parallel circuits.
- Resistance, Temperature coefficient of resistance
- Basic physical concepts of Electricity : protons,neutrons,electrons




1 thought on “What is Ohm’s Law? Ohm’s Law Statement Formula Examples”